Looking for the fahrenheit to rankine formula? Simply put, Rankine (°R) = Fahrenheit (°F) + 459.67. This direct method allows you to convert temperatures from the Fahrenheit scale to the Rankine scale, which is essential in various scientific and engineering fields. In this article, we’ll explore the practical applications of this formula, guide you through step-by-step examples, and share tips for accurate temperature conversion.
Key Takeaways
- The Fahrenheit to Rankine formula conversion adds 459.67 to a temperature measured in Fahrenheit to obtain its equivalent in Rankine, with each degree Rankine being equivalent to one degree Fahrenheit.
- Rankine scale is used predominantly in engineering and scientific fields within the United States for heat computation, with its absolute scale originating at absolute zero, like Kelvin for Celsius.
- Online conversion tools have simplified temperature conversions between Fahrenheit and Rankine, providing fast results and allowing for precision adjustments and bidirectional conversions.
Understanding the Fahrenheit to Rankine Formula
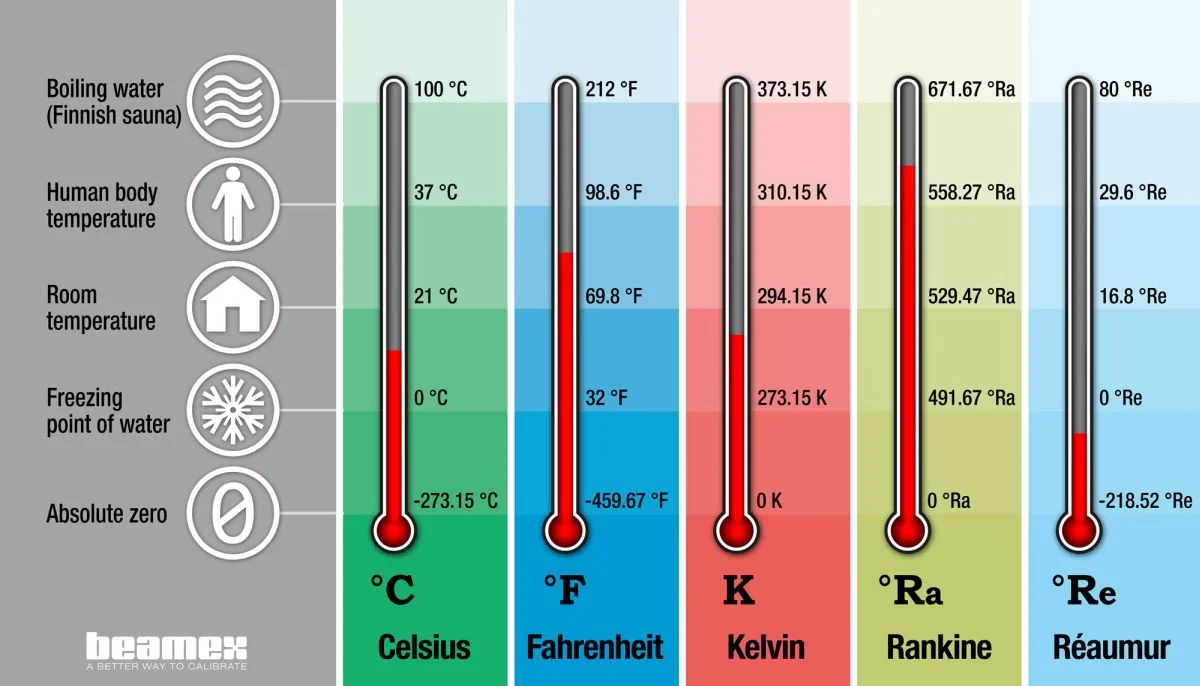
Defining temperature is simple, but measuring it across various scales can be confusing. Thankfully, the Fahrenheit to Rankine formula simplifies this process. The Rankine scale, named after Scottish engineer and physicist William John Macquorn Rankine, is an absolute temperature scale. This means it starts at absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature where all molecular motion ceases. It is related to the Fahrenheit scale, with each degree Rankine equal to a degree Fahrenheit.
To convert Fahrenheit to Rankine, simply use the formula: Rankine (°R) = Fahrenheit (°F) + 459.67.
The Basics of the Formula
Using the Fahrenheit to Rankine formula is a straightforward process. Let’s say you have a temperature of 50 degrees Fahrenheit and you wish to convert it to the degrees Rankine below. A Fahrenheit temperature can be converted to Rankine by adding 459.67, yielding a result of 509.67 °R. This simple arithmetic operation allows for easy and quick conversion between these two temperature scales.
Moreover, modern technology has made this process even simpler. Today, manual calculations are no longer necessary. You can use an online conversion calculator that will do the conversion for you in an instant.
Why Use the Rankine Scale?
The Rankine scale might not be as commonly used in everyday life as the Fahrenheit or Celsius scales, but it holds a unique place in several fields. It is predominantly used in engineering within the United States, especially in fields where heat computations are based on degrees Fahrenheit. For these applications, the Rankine scale is integral for accurate and simplified calculations.
Moreover, as an absolute temperature scale, the Rankine scale has a direct conversion relationship with the Fahrenheit scale. This makes it convenient for working with absolute temperatures in engineering calculations.
Furthermore, the Rankine scale proves particularly useful in scientific applications involving heat computation, where the Fahrenheit scale is traditionally employed.
Step-by-Step Conversion Guide
With a grasp of the Fahrenheit to Rankine formula basics and their importance, we can proceed to its application. The rankine conversion table and process is simple: begin with the Fahrenheit temperature, add 459.67, and the result is the equivalent Rankine temperature.
Converting Common Temperatures
We can apply the theory with a few examples. Suppose we have a typical room temperature of 68 degrees Fahrenheit. Using the formula, we add 459.67 to 68, resulting in 527.67 °R. This means that a room with a comfortable temperature f 459.67 in Fahrenheit would be quite chilly in Rankine!
Another common temperature is the freezing point of water, which is:
- 32 degrees Fahrenheit
- 0 degrees Celsius
- 273.15 Kelvin
- 491.67 °R
Converting this to Rankine gives us 491.67 °R, which is significantly higher than the Fahrenheit value. These examples illustrate how the same temperature can have very different values on different scales.
Tips for Accurate Conversions
Precision is of utmost importance when converting temperatures, particularly in scientific and engineering scenarios. For consistency and precision in calculations, it’s important to use precise values and refrain from premature rounding off.
In addition to careful arithmetic, you can also use a conversion table for quick reference and cross-verifying your calculations. These tables provide pre-calculated values for common temperatures, helping you avoid mistakes and ensure the accuracy of your conversions.
Exploring the Fahrenheit Scale
The Fahrenheit scale plays a key role in our discussion. Named after the German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, this scale was developed in the early 18th century and was a significant improvement over existing scales due to its use of mercury in thermometers.
The zero point on the Fahrenheit scale was defined as the freezing temperature of a brine solution made from a mixture of water, ice, and ammonium chloride. Two key fixed points on the scale are the freezing point of water and boiling points of water, set at 32 °F and 212 °F, respectively. The Fahrenheit scale continues to see usage today in some territories, including the United States.
Key Fahrenheit Temperatures
There are several key temperatures on the Fahrenheit scale that are worth noting. The most well-known of these is the freezing point of water, which is 32 degrees Fahrenheit. This temperature is a common reference point in everyday life, especially in regions where the Fahrenheit scale is used.
Another key for temperature measurement is the boiling point of water, which is defined as 212 degrees Fahrenheit. This temperature is another common reference point, especially in cooking and other household applications. Temperature measurement at these key points, when converted to Rankine, provides a useful way to understand the relationship between the Fahrenheit and Rankine scales.
All About the Rankine Scale
The Rankine scale, like the Fahrenheit scale, has its unique characteristics. This absolute temperature scale starts at absolute zero, the theoretical empty point of water where no thermal energy remains in a substance. It’s based on the Fahrenheit scale but resets at zero at -459.67°F.
A vital feature of the Rankine scale is that a temperature difference of one Rankine degree is equal to one Fahrenheit degree, ensuring an equivalent temperature change on the boiling point of both scales. This makes it easy to convert between them. One significant temperature point on the Rankine scale is the boiling point of water, which is 671.67°R.
Unique Features of the Rankine Scale
One of the most noteworthy features of the Rankine scale is its starting point at absolute zero. This is the theoretical point where no thermal energy remains in a substance, making it an absolute temperature scale. This is similar to how zero point on the Kelvin scale corresponds with Celsius degrees.
The Rankine scale is crucial for precise scientific calculations due to its importance in thermodynamics. It aligns with the third law of thermodynamics, which reflects that absolute zero is unattainable. This makes the Rankine scale a valuable tool in the world of science and engineering.
Comparing Temperature Scales
We’ve looked at the Fahrenheit and Rankine scales in detail, but how do they compare to other temperature scales? Let’s quickly explore this aspect. Absolute zero, the point where all thermal energy ceases, is defined as 0 Kelvin or 0 Rankine. This translates to -273.15°C or -459.67°F.
Meanwhile, a degree Fahrenheit represents 1/180 of the interval between the freezing and boiling points of water on the Fahrenheit scale. To convert from Celsius to Kelvin, you simply add 273.15 to the Celsius temperature, and to convert from Kelvin to Celsius, you subtract 273.15 from the Kelvin temperature. These relationships are crucial for maintaining standardized temperature measurements across different scales.
Conversion between Scales
Though conversions among various temperature scales may appear complex, they become simpler with an understanding of their relationships. The Fahrenheit and Celsius scales intersect at -40 degrees, where the temperatures are exactly the same in both units.
Converting between Kelvin and degrees Rankine is also straightforward due to the direct relationship between the two scales: 1 K = 9/5 °R. Furthermore, the Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero and is offset by -273.15°C compared to the Celsius scale; understanding this relationship is vital for conversions between these two scales.
Online Conversion Tools
Even though grasping the fundamental principles of temperature conversion is crucial, technology has simplified the process of converting between Fahrenheit and Rankine. Online conversion calculators enable users to now convert fahrenheit to rankine instantly, often offering precision up to 5 decimal places to ensure accuracy. All you need to do is enter the temperature in Fahrenheit and hit the ‘Convert’ button.
Some tools even offer bidirectional conversion, allowing for calculations from Rankine back to Fahrenheit, and often include a Rankine conversion table for easy reference.
How to Choose the Right Tool
With a plethora of online conversion calculator and tools available, the challenge lies in selecting the most suitable one. For efficient usage, select a tool that provides instant results without the need to press a submit button. If specific precision is necessary, choose calculators that offer the option to round results to a desired number of decimal places.
Tools supporting both Fahrenheit to Rankine formula and Rankine to Fahrenheit conversions ensure greater flexibility and application range.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding the Fahrenheit to Rankine formula conversion and the principles behind different temperature scales is essential in numerous scientific and engineering contexts. We’ve explored the origins and characteristics of the Fahrenheit and Rankine scales, examined the step-by-step conversion process, and provided tips for accurate conversions. We’ve also compared these scales to others, such as Celsius and Kelvin, and discussed the benefits of online conversion tools. Armed with this knowledge, you now have the tools and understanding needed to master the Fahrenheit to Rankine conversion.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Fahrenheit to Rankine formula?
To convert degrees Celsius to Rankine, you should multiply the Celsius value by 9/5 and then add 491.67 to the result. For example, if the temperature is 25 degrees Celsius, the calculation would be (25 x 9/5) + 491.67 = 536.67 Rankine.
What is the Rankine equivalent of 500 F?
The Rankine equivalent temperature of 500°F is 959.67°R, according to Fahrenheit to Rankine formula conversion table.
Why is the Rankine scale important?
The Rankine scale is important because it is crucial for precise scientific calculations in engineering, especially in fields where heat computations are based on degrees Fahrenheit. It is an absolute temperature scale used predominantly in the United States for these purposes and that’s why its important to learn about the Fahrenheit to Rankine formula.
What are some key temperatures on the Fahrenheit scale?
Key temperatures on the Fahrenheit scale include the freezing point of water at 32 degrees Fahrenheit and the boiling point of water at 212 degrees Fahrenheit.
What are some features of a good online conversion tool?
A good online conversion tool for Fahrenheit to Rankine formula should provide instant results, offer the option to round results to a desired number of decimal places, and support various conversion options such as Fahrenheit to Rankine and Rankine to Fahrenheit.
Related Blogs for Fahrenheit to Rankine Formula:
Thermometers with Mercury: Everything You Need to Know
Precision ASTM Thermometers: Certification and Specification
How to Convert 65 Degrees C to F>
Role of Thermometers in Concrete Curing
How to Convert 70 Deg F to C Easily
How to Convert 158 Fahrenheit to Celsius (158 F to C)
Lab Grade Thermometer for Concrete Testing
Certified Thermometers for Material Testing
Comprehensive List of Biology Laboratory Equipment in 2023
Thermometers Calibrated: Calibrate for Accurate Readings
Convert 900 Degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius (900 F to C)
Master C to F Formula: How to Convert Celsius to Fahrenheit
Digital Humidity and Temperature Meter: Discover the Best
7 Fahrenheit to Celsius: Quick Temperature Conversion Guide
75 Fahrenheit to Celsius Converter: Easy Conversion Method
Easy Guide: Convert 69 Fahrenheit to Celsius Effortlessly
67 F to C: Accurate Fahrenheit to Celsius Conversion Guide
Convert 99.4 F to C: Fahrenheit to Celsius Conversion
Easy K to F Conversion: Your Guide to Kelvin to Fahrenheit
Quick 35 f to c Conversion: Convert Fahrenheit to Celsius
Easy 0 F to C Conversion: Turn Fahrenheit into Celsius Fast
60 Degrees C to F: Quick Conversion Guide
32 Celsius to Fahrenheit: Easy Temperature Conversion Guide
How to Convert 79 Degrees F to C Easily [Conversion Solved]
Temperature Conversions Table: Fahrenheit to Celsius
Celsius to Kelvin: Guide to Accurate Temperature Conversion
Quick and Easy Celsius Calculator for Temperature Conversion
K to Rankine Conversion: Master the Temperature Scales
Conversiones de Temperatura: Convierte Celsius y Fahrenheit
How to Convert 50 Degree Fahrenheit to Celsius [Solved]