Get the Best from Your Lab Vacuum Pump

In today’s fast-paced world of scientific research, laboratories require efficient and reliable equipment to achieve their goals. One such indispensable tool is the lab vacuum pump. These versatile devices play a crucial role in a multitude of applications, from vacuum filtration to freeze drying. To ensure optimal performance and longevity, it’s essential to choose the right vacuum pump for your specific needs and maintain it properly.
This comprehensive guide will help you better understand the various types of lab vacuum pumps, their applications, and how to select the best one for your lab. Additionally, we’ll discuss essential accessories and maintenance tips to keep your vacuum pump running smoothly, ensuring high-quality results and a safe working environment.
Key Takeaways
-
Understand the features and functions of different types of lab vacuum pumps to determine which one is best suited for your application.
-
Consider oil-free/oil-based, chemical resistance, portability and other factors when selecting a lab vacuum pump.
-
Invest in essential accessories, adhere to maintenance requirements and consider budget & size needs when purchasing a laboratory vacuum pump.
Types of Lab Vacuum Pumps
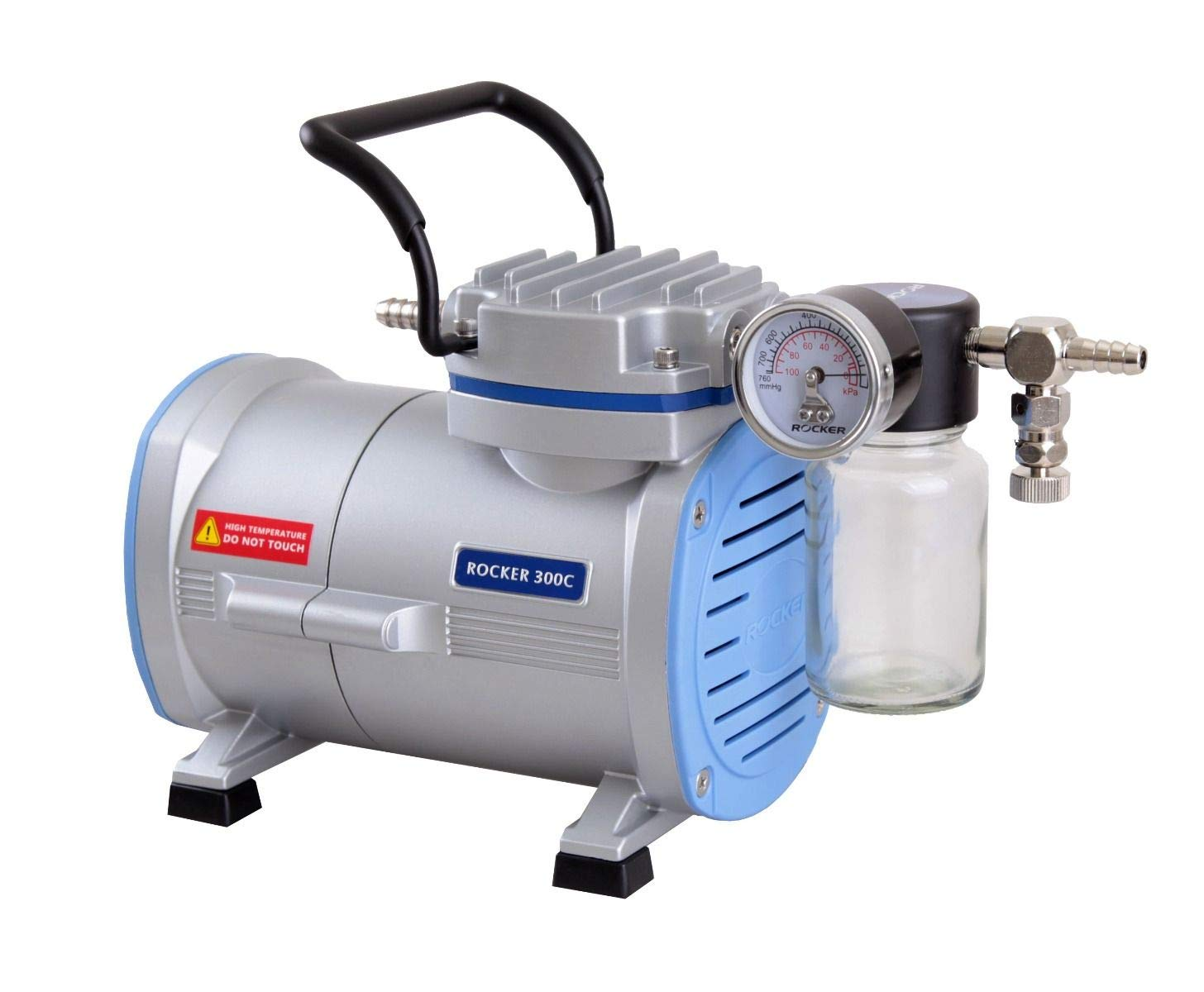

Lab vacuum pumps come in various forms, each with its unique advantages and applications. The most common types include rotary vane pumps, diaphragm vacuum pumps, and scroll vacuum pumps.
Familiarity with their features and functions can guide and assist you in choosing the optimal vacuum pump for your laboratory.
Rotary Vane Pumps
A rotary vane pump is a positive-displacement pump that uses vanes mounted on a rotor to transfer fluids and gases, such as in vacuum aspiration. These pumps consist of:
-
A rotor
-
Vanes
-
Housing
-
Drive mechanism
The rotor is a cylindrical shaft with spring-loaded vanes that oscillate in and out of the rotor slots as it rotates, creating suction and pressure required to move the fluid or gas.
Rotary vane pumps are highly versatile and often used in laboratory settings as a reliable vacuum source. They are dependable, efficient, and simple to maintain, with relatively low noise levels.
Rotary vane pumps work well with many lab products, like FreeZone Freeze Dryers, Protector Controlled Atmosphere Glove Boxes, CentriVap Centrifugal Concentrators, and rapidvap vacuum evaporation systems. Using an exhaust filter with these pumps helps avoid contamination and keeps them functioning correctly.
Diaphragm Vacuum Pumps
Diaphragm vacuum pumps, also known as diaphragm pumps, are oil-free, low maintenance, and suitable for applications that necessitate chemical resistance. These pumps operate without oil, making them highly resistant to chemical substances and more environmentally friendly. Various laboratory settings employ a diaphragm vacuum pump for their oil-free operation.
VACUUBRAND HYBRID™ Vacuum Pumps feature a rotary vane pump and a chemical-resistant diaphragm pump. This combination results in a pump which requires low maintenance and has a long lifespan. This innovative design offers the best of both worlds, providing an ideal solution for laboratories dealing with a wide range of applications and chemical substances.
Scroll Vacuum Pumps
Scroll vacuum pumps, such as the scroll vacuum pump, use two interleaved spiral-shaped scrolls to effectively compress and move gas or liquid. These pumps provide excellent performance and low noise levels, making them suitable for use in sensitive laboratory environments.
Routine maintenance is key to prolonging the lifespan and ensuring the optimal performance of scroll vacuum pumps. Essential accessories, such as filters, traps, and valves, should be included with the pump. Proper upkeep will guarantee smooth operation and prevent potential issues that could hinder your lab’s efficiency.
Applications of Lab Vacuum Pumps

Lab vacuum pumps are integral to a variety of applications, such as vacuum filtration, freeze drying, rotary evaporators, and vacuum ovens. Each application requires different vacuum pump specifications to ensure optimal performance.
Knowing details about these applications and the vacuum pumps best suited for them guides you in choosing the right equipment for your laboratory.
Vacuum Filtration
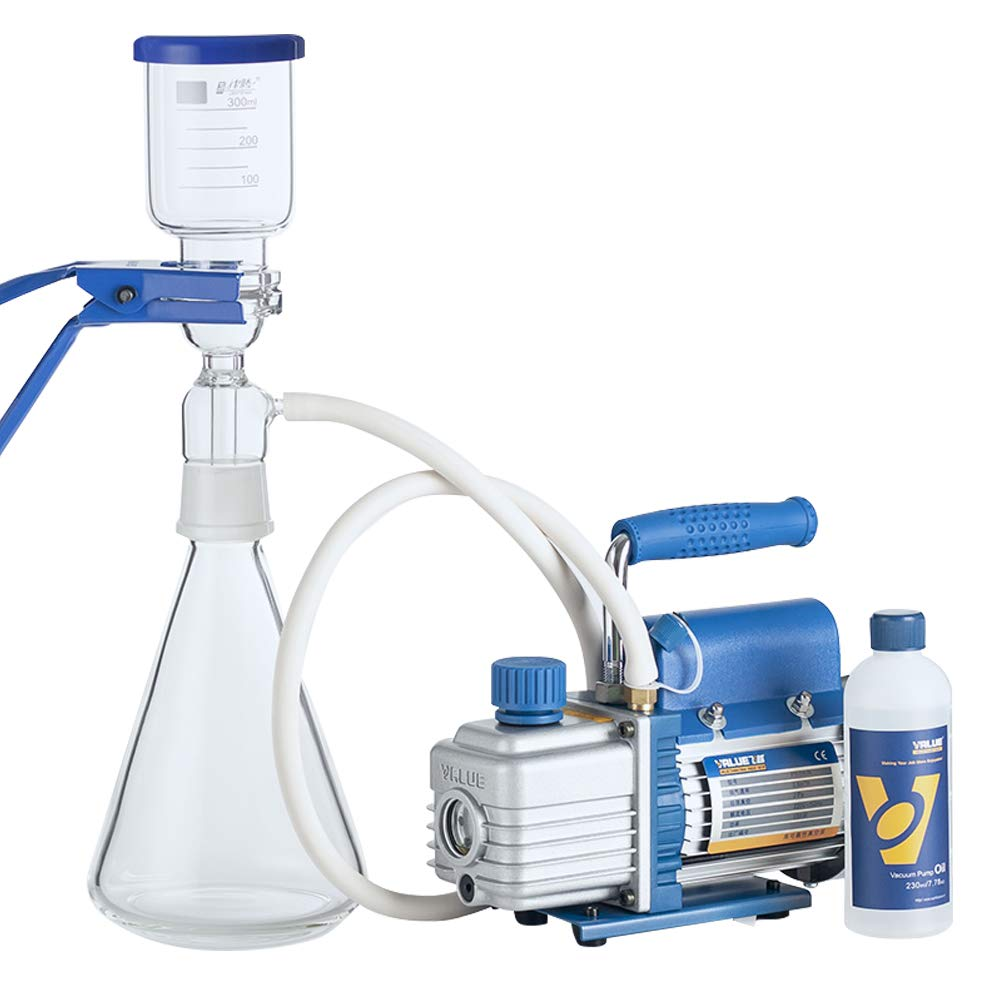
Vacuum filtration is a rapid filtration process used to separate solids from liquids, working by creating a pressure differential across a filter medium by evacuating the air below it. Employing a laboratory vacuum pump for vacuum filtration can enhance productivity by enabling the user to initiate the process and then move away from the area after activating the switch.
Choosing the right vacuum pump for your filtration needs depends on factors such as the type of sample, the desired filtration rate, and the volume of liquid. Considering these factors will help you make an informed decision, ensuring the best results for your specific application.
Freeze Drying
Freeze drying, or lyophilization, is a low-temperature dehydration technique that involves freezing the product and reducing its pressure to remove water or other solvents. Deep vacuum levels are essential for freeze drying, as they enable the removal of solvents without causing any damage to the product. Gel dryers can be used in similar processes, where precise control over temperature and pressure is required.
Maintaining consistent performance from vacuum pumps for freeze drying is paramount to guarantee even and consistent drying of the product. When determining the ideal vacuum pump for freeze drying, consider factors such as:
-
The type of pump
-
The size of the pump
-
The chemical resistance of the pump
-
The portability of the pump
-
Budget considerations
-
Lab size and requirements
-
Brand reputation and support
Considering these factors will help you choose the best vacuum pump for your freeze drying needs.
Rotary Evaporators
A rotary evaporator, commonly referred to as a rotavap, is a laboratory apparatus that removes solvents from samples by means of evaporation. It operates by rotating the sample flask containing the liquid, while a water-cooled condenser effectively cools and condenses the evaporated solvent, allowing for efficient and gentle solvent removal. Rotary evaporators are effective and delicate, offering a straightforward operation with minimal upkeep.
When selecting a rotary evaporator, consider the following factors:
-
Size of the sample
-
Type of solvent being used
-
Desired evaporation rate
-
Allocated budget
These parameters will help you choose the most suitable rotary evaporator system for your laboratory needs.
Enhancing Lab Efficiency with Proper Vacuum Pump Selection
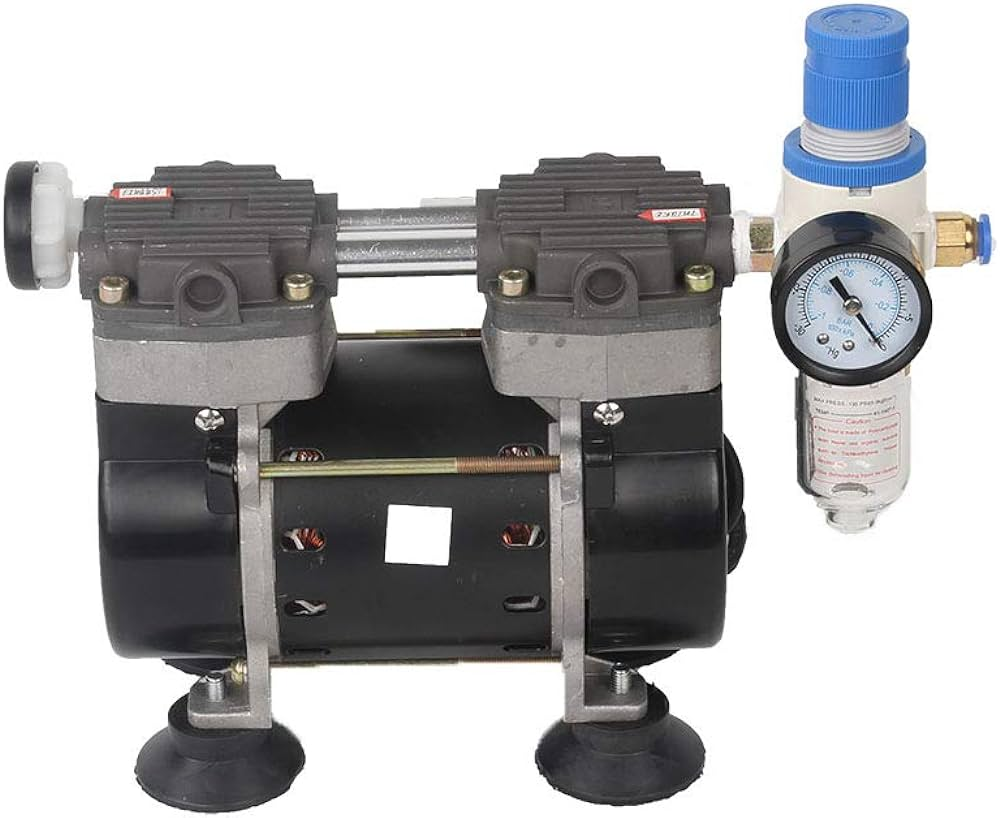

Picking the suitable vacuum pump is vital for boosting lab efficiency and optimal performance. We will delve at length into the considerations for oil-free versus oil-based pumps, chemical resistance, and lightweight and portable options in this segment.
By understanding these factors, you can make a well-informed decision when selecting a vacuum pump that best suits your laboratory’s needs.
Oil-Free vs. Oil-Based Pumps
Oil-free vacuum pumps, such as diaphragm pumps and scroll pumps, require minimal upkeep and are more eco-friendly compared to oil-based pumps, like rotary vane pumps. However, oil-based pumps are capable of achieving greater depths of vacuum compared to oil-free pumps. The choice between oil-free and oil-based pumps depends on the specific requirements of your laboratory and the applications you will be performing.
For instance, oil-free pumps are ideal for applications that require chemical resistance, while oil-based pumps are more suitable for applications involving deeper vacuum levels. Assessing your lab’s needs will help you determine which type of pump is the best fit for you.
Chemical Resistance
Chemical resistance is a critical factor to consider when selecting a lab vacuum pump, especially when dealing with corrosive or volatile substances. Without chemical resistance, the pump may be subject to damage or corrosion, resulting in costly repairs or replacements.
When selecting a chemical-resistant lab vacuum pump, consider factors such as the type of chemicals that will be utilized in the application, the size of the pump, and the budget. Additionally, choose a pump from a reliable brand that offers excellent customer support to ensure a smooth and hassle-free experience.
Lightweight and Portable Options
Light weight and compact portable vacuum pumps, such as the Rocker series and Chemker series, are designed to provide convenient transportability and be a viable alternative for small laboratories or as a backup solution for larger labs. These pumps offer:
-
Ease of transportation
-
Convenience
-
Versatility
-
Energy efficiency
-
Chemical compatibility
-
Noise reduction
Several types of lightweight and portable vacuum pumps are available, including rotary vane pumps, diaphragm vacuum pumps, and scroll vacuum pumps. When making a decision on a lightweight and portable vacuum pump, labs should consider factors such as budget, lab size and requirements, and brand reputation and support.
Accessories and Maintenance for Lab Vacuum Pumps
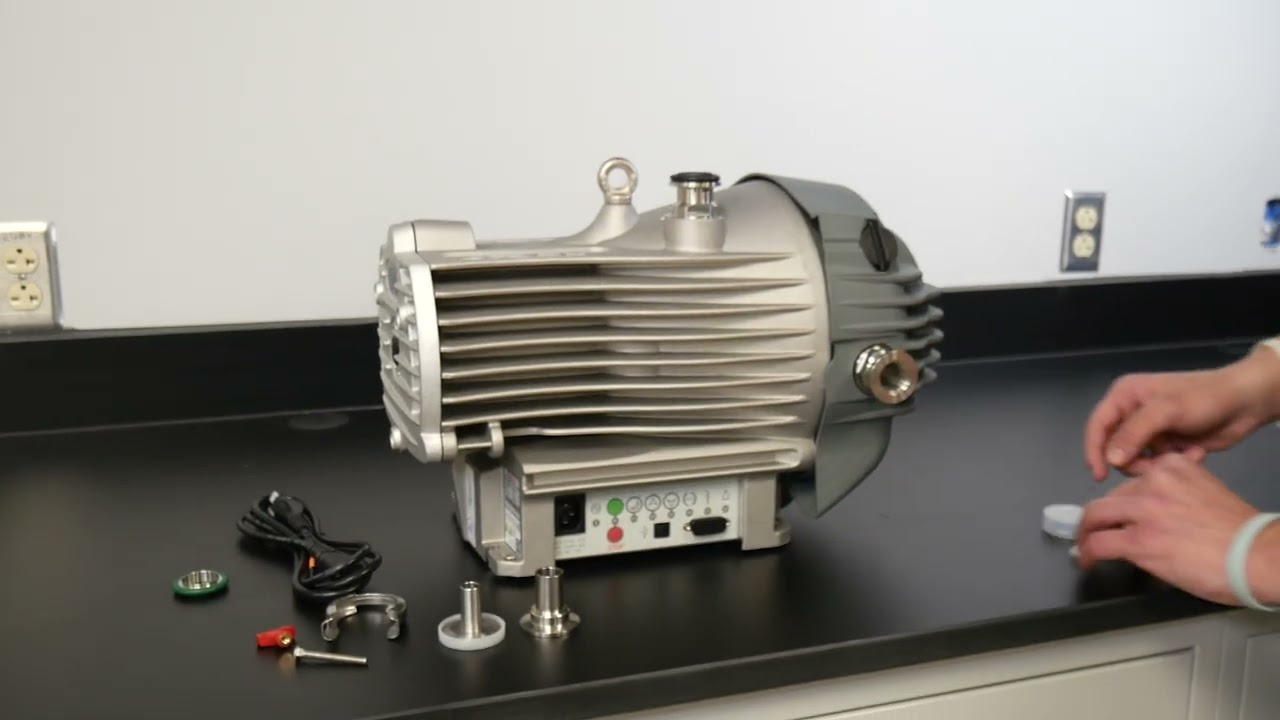

For optimum performance and durability of your lab vacuum pump, equipping it with the correct accessories and carrying out regular maintenance is vital.
In this section, we will discuss essential accessories for lab vacuum pumps and provide maintenance tips designed to keep your pump functioning smoothly.
Essential Accessories
Lab vacuum pumps require essential accessories to ensure optimal performance, such as:
-
Oil change systems: facilitate the swift and effortless replacement of oil in laboratory vacuum pumps
-
Chemical traps: capture and remove chemicals from the vacuum pump exhaust, preventing contamination
-
Dry ice traps: capture and eliminate moisture from the vacuum pump exhaust, ensuring a clean and efficient operation.
Investing in these essential accessories will greatly enhance the performance and lifespan of your lab vacuum pump while ensuring you create a safe and efficient working environment.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is crucial to guarantee the proper and efficient functioning of lab vacuum pumps, as well as to maximize their lifespan and minimize the risk of breakdowns. Maintenance typically involves oil changes, filter replacements, and other routine tasks.
It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s specifications, including adhering to the recommended timeline for oil changes and filter replacements, as well as any other maintenance procedures that may be necessary. By adhering to these instructions, you can ensure your vacuum pump operates optimally and prolong its life, minimizing the risk of breakdowns and costly repairs.
Purchasing Considerations for Lab Vacuum Pumps
Before investing in a lab vacuum pump, factors such as budget, lab size and needs, along with brand reputation and support, should be taken into consideration. Keeping these factors in mind will help you make an informed decision and select the best vacuum pump that meets your laboratory needs.
Budget-Friendly Options
Cost-effective options for laboratory vacuum pumps include:
-
Rocker 300 oil-free pump
-
Rocker 400 oil-free pump
-
Lafil 300C
-
Chemker 300
These pumps are suitable for filtration applications with light weight non-aggressive solvents. They offer increased efficiency, reduced maintenance requirements, and quieter operation compared to oil-based pumps.
In addition to these budget-friendly options, you can also consider the Chemker 200 and Lafil 200C for applications with non-aggressive solvents. By choosing a cost-effective vacuum pump that meets your laboratory’s requirements, you can save money without compromising on performance or quality.
Lab Size and Requirements
When selecting a lab vacuum pump based on lab size and requirements, consider factors such as the dimensions of the lab, the intended use of the pump, and the desired level of vacuum pressure. These factors will help you determine the most suitable vacuum pump for your laboratory.
Additionally, it is important to consider factors such as chemical compatibility, footprint, and control of the pump system, including size, weight, and power requirements. By taking these factors into account, you can select a vacuum pump that is tailored to your laboratory’s specific needs and requirements.
Brand Reputation and Support
When investing in a lab vacuum pump, brand reputation and support services hold significant importance. Various brands offer a range of support services, including installation and maintenance, technical support, and customer service. These services can provide peace of mind, knowing that your product will be supported in the event of any issues.
Customer service and warranties offer reassurance that the product will be repaired or replaced if it fails to meet expectations. Ensuring you choose a brand with a solid reputation and excellent support services will help guarantee a smooth and hassle-free experience with your science lab vacuum pump.
Summary
In conclusion, lab vacuum pumps are essential tools in a variety of laboratory applications. Understanding the different types of vacuum pumps, their benefits, and applications will help you make an informed decision when selecting the ideal vacuum pump for your lab. Additionally, equipping your vacuum pump with the proper accessories and performing regular maintenance will ensure optimal performance and a long lifespan.
By considering factors such as budget, lab size and requirements, and brand reputation and support, you can make a well-informed decision and select the best vacuum pump that meets your laboratory’s unique needs. With the purchase of the right vacuum pump, you can enhance your lab’s efficiency, productivity, and safety, ensuring success in your scientific endeavors.
Certified MTP has an elite selection of lab solutions, showcasing industry-leading brands for centrifuges, desiccators, including the popular Drierite Indicating Desiccant 8 Mesh, 5lb Jar, and all the needed vacuum pumps.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a vacuum pump used for in a lab?
Labs use vacuum pumps to provide suction for filtration and aspiration of samples, as well as reduce vapor pressure to control solvent evaporation.
What is a laboratory vacuum?
A laboratory vacuum refers to systems that provide vacuum to multiple workstations in a laboratory or enough suction to operate Pasteur pipettes and move assays through multiple channels.
What is the pressure of a lab vacuum pump?
The pressure of a lab vacuum pump typically falls within the range of 1.5 Torr to 150 Torr, with low-pressure applications falling between 1.5 and 10-3 Torr and instrument-dedicated pumps able to reach as low as 10-8 Torr.
What are the main types of lab vacuum pumps?
The main types of lab vacuum pumps are rotary vane, diaphragm and scroll pumps.
What maintenance is necessary for lab vacuum pumps?
Maintaining lab vacuum pumps involves regularly changing the oil, replacing filters, and performing other routine tasks to keep them running smoothly.
Related Blogs for Lab Vacuum Pumps:
Suction Filtration: The Basics of Vacuum Filtration
Aspirator Flask: Benefits of Borosilicate Glass Filter Flask
Fire Hydrant Connector Adapters and Fitting
Top Choice for Bulk Rubber Hose: Durability And Flexibility
Top Quality EPDM Hose Solutions for Industrial Applications
Tips for Hose and Handling in Industrial Applications
Hoses for Concrete Pumping: Durable and Flexible Solutions
Advantages of Aspirator Water Vacuum Pumps: Lab Efficiency
