Gravity Convection Oven: Unlock the Benefits

Are you tired of having your delicate samples disturbed by forced air circulation in traditional ovens? Do you need a reliable oven that offers gentle heating for sensitive materials? Enter the world of gravity convection laboratory ovens! These innovative ovens are specifically designed to cater to a wide range of applications, from scientific research to baking. In this blog post, we will explore the benefits and unique features of gravity convection ovens, compare them to mechanical convection ovens, and provide you with tips on how to achieve optimal performance with your gravity convection oven.
Key Takeaways
-
Gravity convection ovens are ideal for delicate drying and heating tasks due to their lower temperature uniformity.
-
They differ from mechanical convection ovens in how hot air is circulated, with gravity relying on natural convection while mechanical uses a fan.
-
Proper placement, installation and maintenance of the oven is necessary for optimal performance. Monitoring and adjusting temperatures can help address common challenges such as uneven heating or disturbance of sensitive materials.
Understanding Gravity Convection Ovens

Designed specifically for drying, sterilizing, or heat treating lightweight materials without the use of a fan, gravity convection ovens have a distinct advantage. Their lower temperature uniformity compared to mechanical convection ovens makes them an ideal choice for delicate drying and heating tasks, particularly when powder samples and materials could be disturbed by forced air. One popular example of a gravity convection oven is Blue M’s Gravity Oven, which is widely used in various scientific applications.
Using three-side heating (right, left, and bottom), these ovens maintain temperature uniformity without needing air or a fan. For example, Blue M Gravity Ovens are used in scenarios that demand no fan or airflow to protect the thermal process, such as when processing lightweight materials or powders.
Another example is the Thermo Scientific Precision Compact Oven, which can heat samples up to 392°F (200°C) and achieve temperature uniformity without the use of a fan.
How Gravity Convection Works
Gravity convection is a natural process where hot air, upon expanding and becoming less dense than the air around it, rises. As the hot air rises and loses heat energy, it begins to fall. This action then leads to repeat of the same process. In a gravity convection oven, this circulation of hot air produces uniform temperatures within the oven chamber without the need for a fan or external force. This makes gravity convection ovens ideal for applications where a fan or other airflow could disrupt the thermal process.
Blue M Gravity Oven models create a distinct natural air convection system. The gravity oven model generates consistent temperatures through the use of perforated stainless steel shelves, without the need for blowers. This gentle approach to heating is perfect for baking delicate materials and sensitive samples that may be disturbed by forced air circulation found in mechanical convection ovens.
Key Components of Gravity Ovens
Gravity convection ovens typically consist of:
-
A stainless steel inner chamber
-
An outer cabinet constructed with MS or GI sheet with corrosion-resistant powder coating
-
A digital temperature controller with a PT100 temperature sensor
The stainless steel inner chamber is designed to provide a durable and dependable cooking environment, ensuring even heat circulation throughout the oven.
The outer cabinet of a gravity convection oven is precision crafted to provide a secure cooking environment, with enhanced durability and longevity due to its MS or GI sheet construction and corrosion resistance powder coating. The digital temperature controller, equipped with a PT100 temperature sensor, ensures precise temperature regulation for optimal performance.
Comparing Gravity Convection and Mechanical Convection Ovens
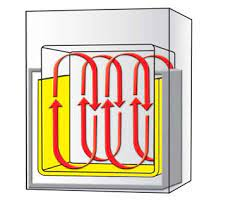
To better understand the unique features of gravity convection ovens, let’s compare them to mechanical convection ovens. The primary distinction between the two lies in how air circulation is achieved. In a gravity convection oven, hot air rises and circulates within the oven chamber without the use of a fan. On the other hand, mechanical convection ovens have an integrated fan that actively circulates the hot air for more uniform temperature distribution.
Gravity convection ovens are suitable for:
-
Baking
-
Roasting
-
Dehydrating food
-
Drying and curing materials, including wood, leather, and ceramics
Mechanical convection ovens, with their forced air circulation, may be less suitable for these delicate applications.
Keep in mind that gravity convection ovens provide less temperature uniformity than their mechanical counterparts. Depending on the specific application, this could be either beneficial or detrimental. For example, if precise temperature control is required, a mechanical convection oven may be more suitable. But if delicate materials or sensitive samples are involved, a gravity convection oven may have less temperature uniformity and be the better choice.
Temperature Uniformity
A significant difference between gravity convection and mechanical convection ovens lies in the level of temperature uniformity they can achieve. Gravity convection ovens offer less temperature uniformity than mechanical convection ovens due to their reliance on natural convection, where hot air rises, resulting in a less uniform temperature distribution.
In contrast, mechanical convection ovens, which incorporate a fan, provide a more uniform circulation of hot air, leading to improved temperature consistency throughout the oven chamber. For applications requiring a higher degree of temperature uniformity, such as baking and roasting, a mechanical convection oven may be more appropriate.
Air Flow and Circulation
Gravity convection ovens and mechanical convection ovens notably differ in terms of air flow and circulation. In a gravity convection oven, the air flow and circulation is achieved through natural convection, wherein hot air rises and produces a vertical airflow pattern without the need for a fan. This natural air flow is ideal for applications where a fan or other airflow could disrupt the thermal process, such as when working with delicate materials or sensitive samples.
On the other hand, mechanical convection ovens utilize a blower fan to actively circulate the air inside the oven, resulting in a more uniform and consistent temperature distribution. While this forced air circulation and thermal process may be more efficient in some applications, it can potentially disturb delicate samples or sensitive materials, making gravity convection ovens the preferred choice for these situations.
Applications and Uses
Gravity convection ovens, also known as laboratory ovens or lab ovens, are typically used in environmental, biological, and clinical laboratories for sterilization, drying, and heat treatment processes where less temperature uniformity suffices. Their gentle heating process makes them ideal for simple drying applications or cases where strong air currents may displace very lightweight materials or samples.
Mechanical convection ovens, on the other hand, are generally used for applications requiring a higher degree of temperature uniformity, such as baking and roasting. Due to their forced air circulation, they may not be the best choice for delicate materials or sensitive samples that could be disturbed by the airflow. In these instances, gravity convection ovens are often the preferred option.
Popular Gravity Oven Models and Brands

Several models and brands of gravity ovens, also known as lab ovens or gravity systems, are commonly utilized in various applications. Some of the most popular brands include:
-
Thermo Fisher Scientific
-
BINDER
- Quincy Lab Ovens
These ovens are known for their precise temperature control, achieve temperature uniformity in heating, and energy efficiency.
When choosing a gravity oven, factors such as temperature range, size, and additional features should be taken into account based on your specific requirements. By choosing a reliable brand and model, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity for your oven, making your investment worthwhile.
Tips for Achieving Optimal Performance with Your Gravity Oven

Following correct procedures for placement, installation, maintenance, and temperature monitoring is key to obtaining the best results from your gravity convection oven.
By taking the time to ensure your oven is functioning optimally, you can prevent common issues and ensure consistent results.
Proper Placement and Installation
The correct placement and installation of your gravity oven are essential for its optimal functioning. It is crucial to verify that the blue m gravity ovens top is level, ensure the door is sealed correctly, and avoid placement in direct sunlight.
Additionally, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for positioning and installing the oven, including:
-
Stacking the upper oven on top of the lower oven using locating studs
-
Installing heat deflectors on both sides of the manifold
-
Properly affixing the oven to the cabinet with screws
-
Installing any additional components, such as shelves or thermometers
Following these instructions will ensure your oven operates efficiently and effectively.
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning

Regular maintenance and cleaning are essential for the longevity and efficiency of your gravity oven. Clean the interior and exterior of the oven regularly using a damp cloth and a mild soap solution. Remove the oven racks and wash them individually in a sink.
Wipe down the control panel surface with hot water, soap, and a soft cloth. Inspect the fan motor and exhaust for proper functioning, and check the door seal for any damage.
Monitoring and Adjusting Temperature Settings
Precise temperature regulation is crucial for achieving optimal performance with your gravity oven. Monitor the temperature by inspecting the thermometer or observing the LED display. Adjust the temperature as needed using the control thermostat knob.
By regularly monitoring and adjusting the temperature settings, you can ensure consistent results and prevent potential issues with your oven.
Common Challenges and Solutions for Gravity Oven Users
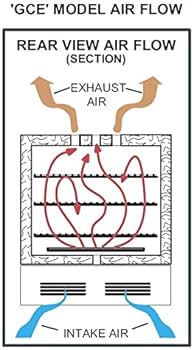
Users of gravity ovens may encounter issues related to temperature control, as temperature uniformity, a limited temperature range, energy efficiency, and restricted airflow.
However, by following proper procedures for accurate positioning and installation, regular maintenance and cleaning, and monitoring and adjusting temperature settings, these issues can be overcome.
Uneven Heating
In a gravity convection oven, uneven heating arises when the heat is not uniformly dispersed across the oven, resulting in areas that are either hotter or cooler than others. This issue can be caused by:
-
Incorrect temperature settings
-
Uncalibrated oven controls
-
Faulty heating elements
-
Issues with the oven’s temperature sensor
-
Problems with the oven control board.
To address uneven heating, adjust the temperature settings, calibrate the oven controls, replace faulty heating elements, check the oven’s temperature sensor, and replace the oven control board, if necessary.
Disturbance of Sensitive Materials
In gravity ovens, disruptions to sensitive materials during the heat treat process can occur due to factors such as over-drying, temperature fluctuations, and the interaction of materials with penetrant substances forced air. To ensure the integrity of delicate materials in a gravity oven, make sure the oven is correctly installed and maintained, and monitor and adjust the temperature settings as necessary.
Additionally, use proper materials for the application and avoid overloading the oven to prevent any potential disturbances.
Summary
In conclusion, gravity convection ovens offer a unique and gentle heating solution for a wide range of applications, from scientific research to baking and drying. By understanding the differences between gravity and mechanical convection ovens, selecting the right oven model and brand, and following proper procedures for placement, installation, maintenance, and temperature monitoring, you can achieve optimal performance with your gravity ovens and ensure consistent results.
Embrace the power of gravity convection ovens and unlock their benefits, whether you’re working with delicate samples in a laboratory or looking for a reliable and gentle oven for your culinary creations. The possibilities are endless with these versatile and efficient ovens!
Certified MTP has the largest selection of lab ovens in their wide selection of Benchtop Ovens from manufacturers such as Quincy Lab Ovens, Despatch Ovens, Lab Companion Ovens and Grieve Ovens.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a gravity convection oven?
A gravity convection oven is a laboratory oven without any fans to circulate air, making it ideal for gentle drying and heating of light-weight materials that may be disturbed by forced air.
What is the difference between gravity convection and mechanical convection?
Gravity Convection is the result of air being circulated naturally by hot air rising, while Mechanical Convection is an oven that uses a fan to circulate air for more uniform temperatures.
How does a gravity oven work?
Gravity ovens use temperature and density differences in heated air to circulate inside the chamber, resulting in reduced levels of temperature stability and uniformity with occasional dead spots.
What is the use of gravity oven?
Gravity convection ovens are designed for applications where forced air would disturb the thermal process, such as drying powders or lightweight materials. These ovens are used for various processes, including aging, burn-in, curing, and moisture testing. Gravity ovens are also ideal for gentle drying and heating of powder samples and many other types of light materials.
How does gravity convection work in an oven?
Gravity convection in an oven works by hot air rising and circulating naturally within the oven chamber, creating a uniform temperature.
Related Blogs to Gravity Convection Oven:
Muffle Furnace: Unlocking the Benefits
Benchtop Muffle Furnaces for Laboratories
The Importance of Material Testing Ovens
Key Considerations for Choosing Your Industrial Oven or Furnace
Ignition Oven: A Guide to NCAT Asphalt Content Furnace Tech
Understanding Rolling Thin Film Oven Testing Equipment
Despatch Oven: The Power of Industrial Ovens and Furnaces
Laboratory Convection Oven: Benefits and Applications
The Benefits of a Lab Convection Oven
Replacing a Sheldon Lab Oven Door Gasket
A Guide to Grieve Ovens and Industrial Oven Manufacturing
An Overview Despatch Oven: The Leader in Industrial Ovens
The Ultimate Guide to Industrial Oven Manufacturers
Find the Perfect Heat Treat Oven for Your Needs
Quincy Lab Ovens: Discover the Benefits
Vacuum Oven: Unlocking the Benefits
The Benefits of a Drying Oven for Industrial Applications
The Benefits of Lab Oven for Heating and Drying
What is Pyrolytic Oven Cleaning and Is It Worth it?
Get the Best Lab Oven for Your Research
Field Oven vs Laboratory Oven: Which is More Accurate?
Industrial Oven: Key Considerations
