Types of Wood Construction Materials for Your Next Build

Understanding the types of wood construction materials is crucial for any build. From the sturdiness of oak to the workability of pine, and the advanced capabilities of engineered wood, this article serves as your concise guide. By highlighting the key characteristics, common uses, and the distinct strengths of different wood materials, you’ll be equipped to choose the best wood for durability, functionality, or aesthetic elegance in your construction project.
Key Takeaways
- Hardwoods and softwoods differ in origin, density, and typical applications; hardwoods are used for durable construction elements while softwoods are preferred for structural purposes due to lightness and flexibility.
- Engineered wood products like LVL, I-joists, and CLT offer modern alternatives to traditional lumber with advantages such as strength, durability, and resistance to warping, providing optimized options for various construction needs.
- Sustainability in different types of wood construction materials is achieved through practices such as using renewable wood resources, opting for FSC-certified wood, and incorporating reclaimed and salvaged wood, which reduce environmental impact and promote responsible forest management.
Distinguishing Hardwoods and Softwoods

The distinction between hardwoods and softwoods lies in their origin, cellular structure, density, and growth rates. Here are some key differences in these types of wood construction materials:
- Hardwoods typically originate from angiosperm trees, which are deciduous and feature broad leaves.
- Softwoods come from gymnosperm trees, such as conifers, that are evergreen and have needles.
- Hardwoods are denser and more durable.
- Softwoods are lighter and more flexible.
In construction, each type of wood has its preferred applications. Hardwoods are favored for projects requiring longevity, such as flooring, decks, and high-quality furniture, while softwoods are commonly used for framing, decking, and other structural applications due to their lighter weight and flexibility. We’ll explore these categories in more detail next.
Types of Wood Construction Materials: Hardwoods
Hardwoods, characterized by their slow growth, density, and durability, can take significantly longer to mature than softwoods—up to 150 years for some species and types of wood construction materials. This slow growth contributes to their stability and durability, making them resistant to decay and less prone to warping and shrinkage, even in moist environments.
Despite being more expensive than softwoods, hardwoods are a suitable choice for various projects, including:
- Cabinet making
- Millwork
- Construction projects necessitating durable and dense wood
- Flooring
- Furniture
- Musical instruments
- Boat building
The applications of hardwood hardwoods, including hardwood trees such as ash wood, are diverse and impressive.
Types of Wood Construction Materials: Softwoods
Contrarily, softwoods like pine and cedar, are characterized by lower density and softer composition, which simplifies the cutting, shaping, and joining processes during construction, helping to preserve the longevity of woodworking tools. These softwood trees typically grow faster than hardwoods, with a readiness for harvest in about 40 years, influencing their widespread availability and reduced cost.
While they’re perfect for framing, flooring, and paneling, softwoods are not confined to these uses. They also serve different industries as raw materials for paper and chemical production and making household furniture. Plus, they take finishes such as paint and stain particularly well, contributing to their popularity for home woodworking projects and crafts.
Popular Hardwoods for Construction Materials
Having established the basics, we’ll now examine some popular hardwoods used in types of wood construction materials. Hardwoods like maple, cherry, and birch are popular for their durability, decorative appearance building wood has, and fire resistance to fire, making them ideal for high-impact structures and surfaces.
Some types of wood and their uses include:
- Maple wood: durable with a fine grain and a light color, making it suitable for wood carvings, musical instruments, and furniture
- Cherry wood: known for its reddish-brown color and versatility, frequently used for indoor construction projects and luxurious furniture pieces
- Birch wood: sporting a pale, creamy color with a smooth texture, and is a durable and strong choice for construction materials.
Types of Wood Construction Materials: Oak Wood
We’ll begin with white oak wood, a favoured option in construction. Recognized for its strength, durability, and flexibility, oak wood has a wide range of uses. One of the reasons oak is preferred is due to its dense, non-porous texture along with its high tannin content, which makes it naturally resistant to water, insects, and fungi.
The characteristics of oak include:
- Resistance to shrinking, making it ideal for stable door and window frames
- A golden color that matures into a silvery shade over time
- A visible wavy grain that can be showcased using a clear finish
Types of Wood Construction Materials: Walnut Wood
Walnut wood is another high-end solid wood known for its dark, rich brown color, stability, and durability. Its naturally dark tone, rich brown colors ranging from light to dark, with occasional purplish hues and dark streaks, and a straight but coarse grain sets it apart. The wood is renowned for its stability, hardness, and durability, being strong without excessive weight, and is relatively easy to work with for woodworking tasks such as turning, carving, and bending.
Used extensively in high-end construction projects, walnut wood is a prime choice for:
- Flooring
- Cabinetry
- Gunstocks
- Decorative items
- Musical instruments
Over the years, walnut wood may undergo a color transformation, lightening to develop a rich honey color, which stakeholders in design and architecture highly regard for its ability to contribute to varying design preferences. This light brown hue adds a unique touch fine texture to any space.
Types of Wood Construction Materials: Maple Wood
Maple wood, known for its aesthetic appeal, is derived from deciduous maples. The special varieties like mountain maple and curly maple, originating at high altitudes, are valued for their unique colors. The wood possesses the following common characteristics:
- Medium weight, approximately 650 kg/m³
- Hard
- Resistant
- Elastic
Annual rings, irregularly spaced pores, and marrow rays between them are distinctive features that make maple wood easily recognizable. Moreover, its versatility extends to its ease of workability and ability to be stained to mimic other wood types, broadening its use from interior design to musical instruments.
Essential Softwoods for Building Projects
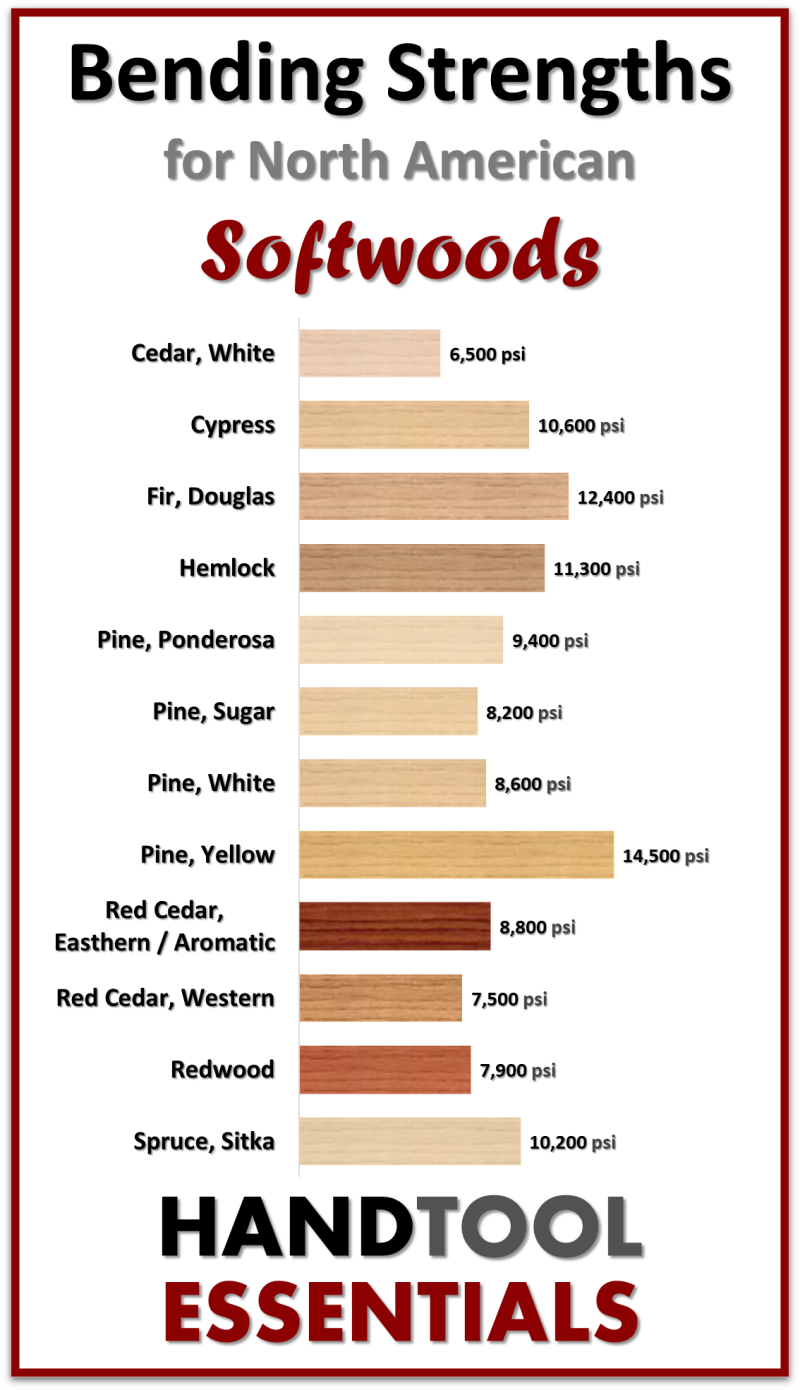
Switching our focus from hardwoods, we’ll discuss key softwoods for construction projects and types of wood construction materials. Softwoods like cedar, fir, and pine are not only affordable and workable but also readily available. For instance, pine wood, widely employed for framing, sheathing, and flooring, is readily available for construction at most major retailers. For exterior construction such as decks, pressure-treated pine is a very common material of choice due to its treatment with chemicals to prevent rot and insects.
Hemlock wood, strong and less prone to wear, tear, and warping red oak, is valued for its ability to develop an appealing color over time and hold stains and finishes effectively. These characteristics make softwoods an essential component for various building projects.
Types of Wood Construction Materials: Cedar Wood
Among the most commonly used softwoods in construction, cedar wood stands out for its inherent resistance to decay, making it an excellent choice for outdoor constructions such household furniture as exterior cladding and decking. The insect-repellent properties of cedar wood protect against infestations, contributing to its common use in outdoor furniture, fencing, and decking.
The pleasant aroma of cedar is not just desirable for its scent but also serves a practical purpose, repelling insects in indoor applications such as closets and chests. However, while cedar offers many benefits including durability and a pleasant scent, it is generally more expensive than many other woods, which can affect budgeting for construction projects.
Types of Wood Construction Materials: Fir Wood
Fir wood, including types like Douglas, white, and balsam fir, is widely used in construction for exterior applications:
- framing
- beams
- doors
- joinery
Thanks to its strength and durability. The most prevalent type of fir used in construction, specifically in the eastern United States, is Douglas fir, recognized for its strength and versatility.
Fir wood is notably celebrated for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it an optimal choice for a variety of home projects. Properly sealed Douglas fir is less likely to warp or split over time than hardwood, enhancing its suitability for structural support in internal settings.
Types of Wood Construction Materials: Pine Wood
Last but not least among softwoods is pine wood. Recognized for its light color and good shock resistance, pine wood is beneficial for construction applications that may experience impact or need to withstand heavy loads. Common uses of pine wood in construction are in high foot traffic areas, including patios and flooring.
As an affordable softwood, pine has the following characteristics:
- Straight grain, making it ideal for projects that involve painting
- Requires seasoning to prevent warping
- Not water-resistant
- Tends to fade with sunlight exposure
- Requires sealing to mitigate these drawbacks
Engineered Wood: A Modern Alternative

We’ll now shift our focus to engineered wood, a contemporary substitute for conventional lumber. Engineered wood is a manufactured product that combines various materials through heat or pressure to create a material that resembles wood in appearance, but is more robust and durable. It includes a variety of products such as Oriented Strand Board (OSB) for sheathing, Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) for solid panels, and LVL for beams, all serving as alternatives to traditional lumber in applications like furniture building, wall paneling, interior doors, flooring, and more.
Engineered wood products are created by bonding wood strands, veneers, lumber, or other forms of wood fiber to produce a composite material designed for specific performance requirements. Due to the controlled manufacturing process, engineered wood is less likely to warp or split, and products like Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) and I-joists offer enhanced strength, weight, and stiffness advantages.
Types of Engineered Wood
Engineered wood products, including I-joists and Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL), are manufactured alternatives to traditional lumber with specific applications in building construction. I-joists are engineered for use as floor and roof joists, utilizing an ‘I’ shape formed by top and bottom flanges connected by a vertical web, providing robustness and stability.
Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) is a construction lumber designed for load-bearing applications, created by bonding together thin wood veneer in multiple layers together, resulting in a strong and uniform construction material. Unlike medium density fiberboard, LVL is specifically engineered for structural purposes.
On the other hand, Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) is an engineered wood product known for its improved thermal performance, which can be advantageous for constructing energy-efficient buildings.
Advantages of Engineered Wood
Engineered wood offers several advantages over traditional wood materials. Enhanced strength and performance consistency in engineered wood is achieved through the distribution of natural defects like knots and splits throughout the material. Furthermore, engineered wood’s dimensional stability means it is less susceptible to warping or distortion due to changes in humidity and temperature.
Besides these inherent properties, engineered wood flooring also offers:
- Flexible design options, including the availability of various long lengths that accommodate wide-open floor plans and large window spaces
- Cost-effective and efficient installations, using conventional framing tools
- Pre-packaged, cut-to-length systems that minimize jobsite waste
Sustainable Wood Choices for Construction
Beyond the physical properties and applications of wood, sustainability is a major concern in today’s construction industry. Both hardwoods and softwoods are renewable resources that contribute to sustainability in construction due to their ability to be replenished. Softwoods usually offer enhanced environmental benefits over hardwoods because they have faster growth rates, which allows for quicker replenishment and sustainable forest management.
Wood is unique as a renewable building material, capable of being grown and harvested in cycles, which supports long-term sustainability in paper production and the construction sector. Moreover, sustainably harvested wood helps in absorbing carbon dioxide, reducing the carbon footprint from construction activities.
Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) Certified Wood
The Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification ensures that wood comes from responsibly managed forests that provide environmental, social, and economic benefits, thereby promoting sustainable forest management. FSC-certified wood supports not only forest sustainability but also benefits workers and safeguards the rights and livelihoods of local and indigenous communities.
FSC certification contributes to market transparency, allowing consumers to make informed decisions based on the sustainability of their wood product purchases. Acquiring FSC certification involves a stringent audit process by independent bodies, verifying adherence to comprehensive criteria for sustainable forest management and chain of custody.
Reclaimed and Salvaged Wood
Reclaimed and salvaged wood are environmentally conscious choices for construction materials, as they help reduce deforestation and maintain biodiversity. Some benefits of using reclaimed wood include:
- Conserving resources by repurposing wood from previously constructed structures such as buildings, bridges, barns, and old gym bleachers
- Reducing waste in landfills
- Preserving the unique character and history of the wood
- Supporting sustainable and responsible building practices
By choosing reclaimed wood, you can contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly construction industry.
On the other hand, salvaged wood derives from trees that have naturally fallen or have been removed from urban settings, and often scrap wood comes in larger dimensions, offering unique opportunities for construction uses. Both reclaimed and salvaged wood support recycling and smart reuse in the building industry, contributing significantly to waste reduction and environmental preservation.
Tips for Selecting the Right Wood for Your Project
Equipped with all this information, you may be pondering on how to select the best wood for your project. Selecting the right wood involves considering factors like:
- Hardwood vs. softwood
- Natural features
- Moisture content
- Nominal vs. actual dimensions
For instance, hardwoods are valued for natural beauty and their superior strength, which enables them to support heavy use, suitable for structural elements and load-bearing projects.
When assessing building wood for a project, it’s important to consider the following:
- The wood’s natural features, such as grain and color, without coatings or treatments
- The wood’s moisture content, as high moisture can lead to changes in appearance and potential damage as it dries
- The nominal and actual dimensions of lumber may differ, which is crucial when planning and ordering materials for a build
Taking these factors into account will help determine the suitability of the specific wood used for your project.
Summary
So there you have it! A comprehensive guide to the world of wood used in construction. From hardwoods to softwoods, engineered wood to sustainable choices, we’ve covered a wide spectrum of information. Whether you’re embarking on a construction project or simply want to expand your knowledge, we hope you’ve found this guide enlightening. Remember, the right wood can make all the difference in your home construction or project, so choose wisely!
View the full line of Sledge Hammers, Digging Bars, Crow Bars, Pry Bars, Brick Masonry, and Landscape Tools
Certified MTP also offers a full line of Construction Shims, including horseshoe shims, wood shims, Wobble Wedges, clear plastic shims, Precast Shims, Leveling Shims, Aluminum Shims, and Key Slot Shims.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of wood used in construction?
The most used types of wood for construction include pine, cedar, and redwood. Each type offers different characteristics such as durability and resistance to decay.
What are the 5 materials made of wood?
Wood can be used to make houses, furniture, paper, pencils, and doors, among other materials, making it a versatile material for various purposes.
What kind of wood is used for carpentry?
Pine is a common and suitable wood for carpentry due to its durability, affordability, and sustainability. It is relatively soft and easy to carve, making it a popular choice for woodworkers.
What is the top 10 hardwood?
The top 10 hardwoods include Hard Maple, Soft Maple (Red Maple), Ash, Sassafras, Cherry, Hickory, Walnut, and Butternut. They are popular choices for both decorative pieces and furniture making various woodworking projects.
What is the main difference between hardwoods and softwoods?
The main difference between hardwoods and softwoods is that hardwoods come from deciduous trees and are denser, while most softwoods come from evergreen trees and are lighter and more flexible.
