Welcome to the fascinating world of soil testing! Our ability to construct towering skyscrapers lay down highways, or simply plant a garden hinges on our understanding of the ground beneath us. The secret to this understanding? An ingenious device called the Hand Vanes tester.
Key Takeaways
- Hand vanes are reliable tools for measuring soil’s shear strength with an accuracy rate of 10%.
- Shear strength is critical in determining the stability and load-bearing capacity of soils, which have various applications.
- Hand vanes must be operated by a qualified operator using high-quality equipment to ensure accurate results. Additional features can also enhance performance.
Understanding Hand Vanes
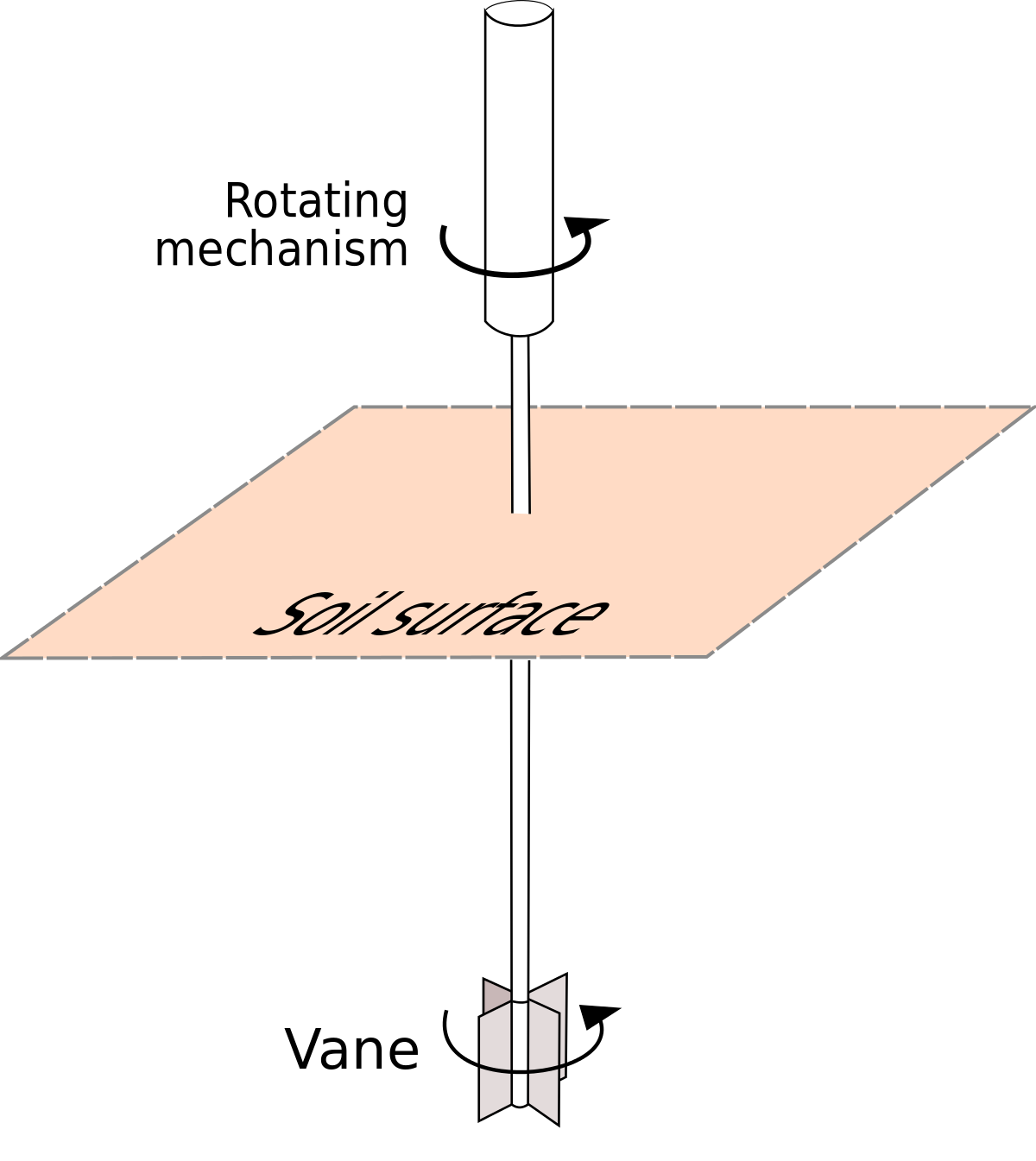
An integral part of any engineer’s toolkit, hand vanes are quick and efficient tools for assessing the stability of foundations, excavations, and trenches in clay soils. These tools measure the soil’s shear strength, a concept akin to die shear testing.
The hand vanes come in four distinct sizes, each with a designated effective range, catering to a wide array of soil types and conditions. Despite its simplicity, the hand vane tester boasts an accuracy level of approximately 10%, making it a reliable tool for rapid field assessments.
Components of a Hand Vanes
A typical hand vane consists of four main components:
- A vane: measures the shear strength of soil by being inserted into the soil and rotated to gauge the soil’s resistance to shearing forces.
- A vane rod: connects the vane to the torque handle.
- A torque handle: applies torque to the vane rod, allowing the vane to be rotated.
- A dial gauge: measures the torque applied to the vane rod, providing a reading of the soil’s shear strength.
Each part plays a crucial role in ensuring the tester’s mechanical reliability during soil testing.
The vane shear test apparatus consists of several components that work together to determine the undrained shear strength of cohesive soils. These components include:
- The handle: This provides a grip for the user and helps in the application of torsional force to the soil sample under test.
- The torque head: This is attached to the handle and is responsible for rotating the vane during the soil test.
- The indicator: This works in conjunction with the torque head to provide a quantitative assessment of the soil’s shear strength. It measures the necessary torque required to rotate the vane during the test.
By using these components, the vane shear test apparatus allows for the accurate determination of the undrained shear strength of cohesive soils, while the die shear test, utilizing a die shear and tool, focuses on other aspects of material testing.
Keep Reading: Advanced Soil Testing Equipment for Geotechnical Labs.
Types of Hand Vanes
Hand vanes come in several different sizes and various types, each catering to specific needs. The standard hand vane is valued for its precision, ease of use, and versatility for both laboratory and field environments. For those who value convenience, pocket hand vanes are a compact and portable design that fits right in your pocket or small bag.
As technology has advanced, so too has the humble hand vane tester. Digital hand vanes offer accurate measurements of soil characteristics like load compression and displacement, making them perfect for field conditions. These modern tools have revolutionized the way we conduct vane shear testing on fine-grained sediments.
The Importance of Shear Strength in Soil Testing
In soil testing, shear strength serves as a fundamental parameter. It helps determine the soil’s resistance to deformation under shear stress, a key factor in assessing the stability of slopes and designing earth-retaining structures. The higher the shear strength, the greater the soil’s stability and reduced susceptibility to failure or collapse. This makes shear strength a critical consideration in the design of secure and stable geotechnical structures like retaining walls, foundations, and slopes.
Moreover, shear strength directly impacts the soil’s load-bearing capacity. As the shear strength of soil increases, so does bond strength and its ability to withstand and support loads. This relationship is influenced by factors such as the angle of internal friction and the soil’s compressive strength. To measure this crucial property, methods such as the direct shear test or box shear test are employed, with hand vane testers being an essential tool for these assessments.
Applications of Shear Strength Measurements
Several industries widely use shear strength and bond strength measurements due to their diverse applications. In the field of construction, they ascertain the capacity of materials to withstand shear forces, forming the blueprint for the formulation and specification of structural elements such as beams and plates.
In geotechnical engineering, shear strength is employed for multiple purposes, including foundation design, slope stability analysis, and retaining wall design. Additionally, it plays a significant role in environmental assessments by determining soil stability, potential for soil erosion, and design of earth retaining structures.
More Read: Essential Equipment for Soil Testing: Your Ultimate Guide.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Hand Vanes for Soil Testing
Hand vane testing, while straightforward, requires a methodical approach. The process initiates with the preparation of the soil sample, which should be contained and leveled on the base of the hand vane tester. Then, the vane testing process involves the following steps:
- Insert the vane into the soil sample.
- Apply torque by rotating the vane.
- Record the readings.
- Calculate the shear strength according to the manufacturer’s guidelines or using the appropriate formula.
Interpretation of results involves comparing the vane strength with the penetration depth. The undrained shear strength is calculated using the measured torque, vane dimensions, and specific formulas. However, observing precautions like avoidance of torque application during vane thrust and refraining from testing soils prone to drainage is crucial.
Preparing the Soil Sample
The preparation of the soil sample for testing constitutes a crucial step. It involves:
- Use appropriate tools to excavate holes and take a sample from each depth.
- Ensuring the tools are clean to prevent contamination.
- Avoiding common errors such as collecting samples from excessively wet soil and inadequately mixing the soil cores.
After collection, soil samples should be:
- Stored in a refrigerator or cold room to preserve their original moisture content and temperature
- Handled carefully to ensure they are undisturbed and accurately represent in-situ conditions
- Stored in sealed containers, labeled with pertinent details
- Promptly transported to the testing laboratory.
The selection process of the soil sample location also impacts the testing results, introducing potential variations in soil composition, moisture content, and density across different locations of a site.
Performing the Test
Performing the test involves the following steps:
- Carefully insert the vane into the soil, ensuring it is fully embedded.
- Rotate the vane using a torque wrench, applying a uniform force.
- Apply torque by rotating the vane inside the soil specimen at a prescribed rate, such as 0.1 degrees per second, to ensure accurate measurement of the shear strength.
Measurements during the test are recorded using tools such as Vernier calipers to measure the vane’s diameter and height, assess the sensitivity of contact with the soil sample, and capture the data for analysis. However, it’s essential to avoid common errors such as ensuring minimal friction during the test, performing the test in appropriate soil conditions, and adhering strictly to the testing procedures.
Interpreting Results
When interpreting the results of a hand vane test, it’s important to realize that the test is best suited for soils with a low shear strength, typically below 0.3 kg/cm2. The results provide an estimation of the undrained shear strength of fully saturated clays without disturbance, based on ASTM D 2573-72.
A high shear strength value indicates that the soil exhibits strong resistance to shearing forces, suggesting its cohesive nature and ability to endure substantial stress without undergoing deformation or failure. Typical shear strength values correspond to the anticipated range for shear tools for a particular soil type and are derived from standardized protocols or classifications.
Atypical values indicate uncommon soil behavior, requiring comparison with established benchmarks for the specific soil being tested or examined. Differences in shear strength values have a substantial impact on soil analysis as they influence stability assessments of slopes and structures, bearing capacities for foundational support, and contribute to soil classification systems.
You may also read: Best Soil Testing Equipment for Accurate Land Analysis.
Factors Affecting Hand Vane Testing Accuracy
The accuracy of hand vane testing can be influenced by several factors. These include the qualifications of the operator, the soil conditions, and the quality of equipment used. An operator’s proficiency can significantly impact the accuracy of hand vane testing results. A proficient and seasoned operator will guarantee proper vane insertion and steady, uniform rotation, reducing the likelihood of errors and disruptions that could distort the results.
Soil conditions, including factors such as substrate properties:
- soil strength
- cohesion
- effective stress conditions
- degree of saturation
- overconsolidation ratio
play a crucial role in influencing the precision of hand vane tests. Fine-grained clays, silts, and other fine geomaterials can disrupt the precision of hand vane testing results. Soil granularity can also influence the shear strength measurements derived from the hand vane test. Furthermore, the temperature of the soil holds potential influence on the shear strength of cohesive soils, extending to the undrained shear strength and the preconsolidation pressure.
Qualified Operator
Hand vane testing greatly benefits from a skilled operator. Their competence ensures proper vane insertion and steady, uniform rotation, reducing the likelihood of errors and disruptions that could distort the results. However, operators can encounter several common errors, including:
- Incorrect positioning or insertion of the vane into the soil
- Inadequate application of torque
- Neglecting to allow the vane to reach maximum torque
- Insufficient cleaning of the vane between tests
Through their expertise, a skilled operator can analyze the outcomes of hand vane testing by evaluating the undrained shear strength of saturated clay and silt soils. This guarantees a more dependable comprehension of soil stability and bearing capacity.
Soil Conditions
By altering the soil’s strength and friction, the soil’s moisture content can affect the accuracy of hand vane testing. Dry soil tends to be more compacted and cohesive, exhibiting higher strength, while wet soil is looser with reduced cohesion, leading to lower strength measurements.
Certain soil types, such as clay and silt, can result in less precise outcomes during hand vane testing. The state of the soil, whether it is loose or dense, also influences the shear strength measurements derived from the hand vane test.
Additionally, the temperature of the substrate of the soil holds potential influence on the shear strength of cohesive soils, extending to the undrained shear strength and the preconsolidation pressure.
Equipment Quality
To ensure accurate and reliable measurements in hand vane testing, the quality of the equipment used plays a key role. High-quality hand vane equipment should have the following features:
- Accurate measurements
- Durable construction
- Ease of use
- Adjustable torque
- Calibration capability
- Portability
- Light weight
- Compatibility with various accessories
Having supplied equipment with these features will minimize errors and inconsistencies, leading to more precise and trustworthy results.
Proper maintenance of the hand vane tester is also critical. Here are some steps to follow:
- Clean the tester after each use.
- Inspect the tester for any damage.
- Regularly lubricate the tester.
- Store the tester in a dry environment.
- Periodically calibrate the tester according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Calibrate the tester on an annual basis to guarantee the accuracy of torque readings and measurements.
Tips for Choosing the Right Hand Vane Tester
It’s a crucial step to select the right hand vane tester. Factors such as accuracy, measurement range, ease of use, durability, portability, price, and reviews/recommendations should be considered. According to research, some of the top hand vane tester brands are:
- Humboldt
- Royale IJkelkamp
- Alpha Omega Electronics
- Turf-Tec
- SCCS Survey
- Impact Test
Additional features that can enhance the functionality of a hand vane tester include:
- A direct-reading scale with a maximum-reading pointer
- A lightweight carrying case
- Digital readouts for precise measurements of soil properties
- Data storage facilities for easy retrieval and analysis of data
- GPS capabilities for precise location tracking, enhanced data management, improved site characterization, and streamlined workflow.
Comparing Different Brands and Models
It’s crucial when selecting a hand vane tester to compare different brands and models. Price comparison is particularly important due to the substantial variation in the cost of hand vane testers across different brands, which can impact the overall budget for essential equipment. To compare prices effectively, it is advisable to collect price information from a range of suppliers and manufacturers to determine the most favorable deal.
While there may be variations in features and capabilities among different brands and models, all hand vane testers are intended for the general task of measuring soil nutrients, rather than specializing in specific soil types. However, different brands and models may present varying features and capabilities, making it essential to consider the unique needs of your soil testing activities.
Considering Additional Features
The functionality of a hand vane tester tool can be enhanced by considering additional features. Digital readouts offer precise measurements of soil properties, eliminating the need for manual interpretation of analog readings. The inclusion of data storage facilities allows for easy retrieval and analysis of data, crucial for evaluating the undrained shear strength of fine-grained clays and silts or other fine geomaterials.
Additional functionalities that can significantly improve the testing process include:
- A microprocessor-controlled drive system
- Keyboard entry for convenient operation
- Pause and speed reset during tests
- RS 232C interface for data transfer
- Operator programming of speed and control functions
- Self-test diagnostics
- Multiple vane sizes
- An extension rod for varied testing options
- Portability for field use and tested reliability
Furthermore, GPS capabilities provide precise location tracking, enhanced data management, improved site characterization, and streamlined workflow.
Case Studies: Hand Vane Testing in Real-Life Scenarios
Hand vane testing serves not only as a laboratory exercise but also as a solution to real-world problems. It is utilized in construction site soil evaluations to perform the vane shear test, determining the undrained shear strength of soils in both undisturbed and remolded samples. This information is crucial for understanding soil stability and load-bearing capacity, guiding decision-making in construction projects.
In environmental impact assessments, hand vane testing is employed to measure the undrained shear strength of saturated clay and silt soils, providing crucial data to comprehend the soil’s properties and potential environmental impact. This facilitates a thorough evaluation of the environmental impact, particularly for projects involving construction and land development in clay-rich areas.
Construction Site Soil Evaluation
For the safety and durability of structures at construction sites, it’s crucial to understand soil stability. Hand vane testing is a common method employed to assess this characteristic by measuring undrained shear strength. Load-bearing capacity also influences construction project planning, determining the maximum load that the soil can safely withstand.
Hand vane testing has been performed and employed in various construction projects, including:
- Assessing the shear strength of cohesive soils in geotechnical engineering
- Examining soil slope and embankment stability
- Evaluating soil compaction during road construction
- Testing soil-cement mixtures in pavement projects.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Hand vane testing has a critical role in environmental impact assessments. By ascertaining the shear strength properties of soil, it aids in evaluating the stability and potential effects of soil in diverse environmental endeavors. It also contributes to the identification of environmental hazards associated with soil conditions by providing an indication of the in-situ undrained shear strength.
Hand vane die shear testing is employed in environmental impact assessments to measure the undrained shear strength of saturated clay and silt soils. This information informs assessments on the potential for erosion, slope failure, and other environmental risks. It has been utilized in various methods, including the examination of soil shear strength characteristics, evaluation of shear strength in wetland areas, and the performance of vane shear testing on in situ sediments.
Summary
In conclusion, hand vane testing is an indispensable tool in assessing soil stability and load-bearing capacity. It requires a skilled operator, specific soil conditions, and high-quality equipment to ensure accuracy. By comparing different brands and considering additional features, you can select the best hand vane tester for your needs. Real-life applications in construction sites and environmental impact assessments showcase the practical value of this tool in our daily lives. With the right knowledge and equipment, you can unlock the secrets of the soil beneath and make informed decisions that affect our environment and the structures we build.
Certified MTP has the largest selection of soil testing supplies, showcasing industry-leading brands for Hand auger tools and soil sampler equipment, Soil Moisture Testing Equipment, field density test equipment, Soil Penetrometers, Soil Strength Test Equipment, and Sand Cone Test Equipment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a hand vane test?
The Hand Vane Test is a tool used to measure the shear strength of cohesive soils by pushing a vane and rod vertically into the soil and rotating it at a slow rate. It measures the torque at regular time intervals until a maximum torque is reached. This testing method can be done both in-situ or on undisturbed soil samples in a lab setting.
What is the vane shear test used for?
The vane shear test is used to measure the undrained shear strength of cohesive soil, particularly soft clays. It can be conducted in-situ or in a laboratory setting, and is simple, quick, and cost-effective.
How do you use Torvane?
Torvane is a testing kit used to determine undrained shear strength by inserting a vane into soft sediment and rotating it until the sediment fails. It is suitable for both field and laboratory settings, accurately measuring shear strength in test pits, trenches, excavations, and more.
What size are shear vanes?
Shear vanes are available in two sizes, 19 mm and 33 mm, for use with Geotechnics’ Shear Vane testing equipment. The 33 mm blade is used in softer materials (0 to 40 kPa) while the 19 mm blade is suitable for up to 220 kPa. An alternative size is 150-by-75-millimetre (5.9 in 3.0 in) for soils with shear strengths up to 50 kN/m2 and 100-by-50-millimetre (3.9 in 2.0 in) for stronger soils.
What are the different types of hand vanes?
Hand vanes come in various types such as standard, pocket, and digital models, offering a range of different features and benefits to suit individual needs.