Asphalt material, familiar yet complex, is the backbone of modern roadways. This article cuts through the complexity to explain the sturdy mix of aggregates and bitumen that withstand wear and tear. We explore why asphalt is a go-to for builders and how it fits into a sustainable, technological future. Get ready to gain a solid understanding of asphalt’s importance without overwhelming details.
Key Takeaways for Asphalt Material
- Asphalt concrete is made up of aggregates, binders, and fillers that create a durable paving material, capable of withstanding heavy traffic and varying weather conditions.
- The production of asphalt material includes hot, warm, and cold mixes, each designed for specific applications, with warm mix asphalt being notable for its environmental benefits due to lower production temperatures.
- Advancements in asphalt material technology, such as self-healing asphalt and eco-friendly options like Foamix using reclaimed materials, exemplify the industry’s innovations and commitment to sustainability.
The Composition of Asphalt Material

Asphalt concrete, a seemingly simple black material, is more complex than it appears. It’s a carefully crafted blend of aggregates, binders, and fillers, each component playing a critical role in providing a stable structure for various paving applications using asphalt materials.
Providing structure and stability, aggregates consist of sand, gravel, and crushed rock. Meanwhile, the bitumen binder acts as a sticky substance that holds these aggregates together. This combination results in a stiff and durable material that can withstand the daily rigors of heavy traffic and fluctuating weather conditions.
Bitumen: The Binding Agent
Imagine a giant jigsaw puzzle, where each piece is an aggregate. Now, think of bitumen as the magic glue holding these pieces together. Bitumen is a thermoplastic binder with unique properties that allow it to liquefy when heated and solidify when cooled. Its performance is influenced by factors such as viscosity, hardness, and adhesion, each playing a pivotal role in the durability and performance of the asphalt material.
This binding agent enables the transformation of a mere collection of rocks into a smooth, sturdy roadway.
Aggregates in Asphalt Material: Strength and Stability Providers
Aggregates in asphalt material are akin to the bricks in a brick wall. They provide the primary load-bearing capacity, with their shape, size, and texture directly impacting the asphalt’s overall performance. To achieve the desired pavement strength, stiffness, and durability, the selection of appropriate aggregates is vital.
From the mineralogy to surface texture, every characteristic of the aggregate influences the durability of the asphalt, making it capable of withstanding vehicular pressure and avoiding cracking.
The Role of Recycled Materials
In an era where sustainability is paramount, the asphalt material industry is leading the way with its use of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP). Utilizing RAP in asphalt mixtures not only minimizes the need for new materials but also reduces waste, enhancing the value of sustainability in the road construction industry. In fact, asphalt is recognized as one of the most sustainable construction materials, largely due to its capability to be fully recycled.
This eco-friendly initiative exemplifies an example of how the asphalt industry is contributing to a more sustainable future.
The Science Behind Asphalt Material Mixes
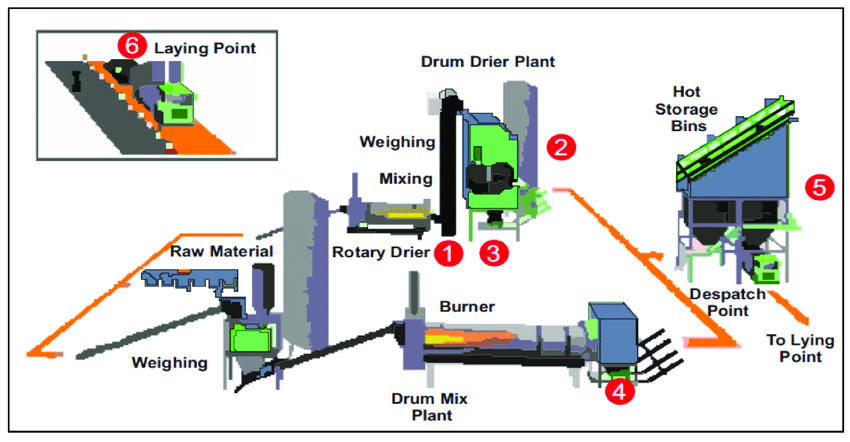
Just as a chef carefully selects the ingredients and cooking methods to create the perfect dish, the creation of asphalt involves a precise selection of materials and production methods. Asphalt mixes used for paving come in three main types: hot, warm, and cold. Each type has its own specific application and benefits. Each type is designed to meet specific project needs and performance requirements, with advanced protocols like the Superpave system enhancing the durability and performance of these mixes.
Hot Mix Asphalt Material: High Temperatures for Strength
Hot mix asphalt is akin to a phoenix rising from the ashes. It’s produced by heating aggregates to decrease the viscosity of the binding agents, allowing the mixture to become more fluid while removing moisture. The optimal mixing temperature for hot mix asphalt is between 200-350 degrees Fahrenheit, pivotal for maintaining the material hot during paving and compaction to ensure quality.
This high-temperature process results in a smooth, durable surface, essential for safe transportation infrastructure.
Warm Mix Asphalt Material: A Sustainable Choice
Warm mix asphalt (WMA) is the eco-friendly cousin of hot mix asphalt. It’s produced at significantly lower temperatures, resulting in reduced fuel consumption and fewer greenhouse gas emissions during production. But despite its lower production temperatures, WMA doesn’t compromise on quality or performance. In fact, its reduced viscosity facilitates easier compaction and allows for hauling the mix over longer distances, potentially lowering overall transportation costs.
Over 40 states within the United States, including Virginia, have embraced and developed this sustainable paving solution, underscoring WMA’s growing acceptance.
Cold Mix Asphalt Material: Versatility in Repair Jobs
Cold mix asphalt is the versatile workhorse of the asphalt family. Thanks to a blend of quarter-inch chip and proprietary oil, it maintains a workable softness across seasons, making it ideal for pothole patching in a variety of weather conditions. It’s not just its pliability that makes it a go-to choice for repair jobs.
Cold mix asphalt is formulated based on specific needs and usage, ensuring a customizable repair solution that can be prepared and stored for future use, offering versatile applications from everyday maintenance to major paving tasks.
The Importance of Quality Control in Asphalt Material Production

Quality control is the unsung hero of asphalt production. It’s a system that monitors and adjusts production processes to meet high-quality levels required by specifications. From sampling and testing mixtures to employing unbiased methods like representative sampling and random sampling, quality control is an integral part of the production process.
These meticulous checks and balances ensure the consistency, durability, and safety of paved surfaces.
Testing for Consistency
Testing for consistency in asphalt is akin to a detective investigating a case. It involves evaluating its consistency, viscosity, and purity, crucial for controlling its behavior during transportation and paving. The gradation and binder content tests involve separating asphalt binder from aggregate, a process that acknowledges the impact of material and sampling variability on test results.
Such meticulous testing guarantees that the final asphalt mix is not only consistent but also meets the high-quality standards required to produce it for diverse applications.
Aggregate Processing: Ensuring Durability
Processing aggregates for asphalt production is a delicate balancing act. It’s about maintaining their durability and angularity to ensure the structural integrity of the asphalt. Aggregate percentages sometimes require adjustments during plant production to achieve the specified volumetrics of the asphalt mix and to compensate for changes like aggregate abrasion.
Such careful processing guarantees the durability of cars on asphalt surfaces, enabling them to withstand daily wear and tear.
The Impact of Material Quality on Safety
Material quality is to asphalt what the foundation is to a building. It impacts the safety and longevity of asphalt surfaces, with recycled materials contributing to increased durability and reduced maintenance needs. Smooth and well-kept asphalt surfaces lead to more efficient driving, requiring less fuel which results in fewer pollutant emissions.
Thus, the quality of materials used in asphalt production plays a crucial role in not just the longevity of the pavement but also in promoting safety and environmental health in heavily trafficked urban areas.
Innovations in Asphalt Technology

Innovation is the lifeblood of progress, and the asphalt industry is no exception. Advances in asphalt technology and research have led to the development of innovative solutions such as electric vehicle-charging pavements, pollution-absorbing surfaces, and self-healing asphalt.
These technological advancements not only augment the material’s performance and functionality but also contribute to more sustainable technologies and efficient infrastructures.
Self-Healing Asphalt
Imagine a road that can heal its own cracks, much like a living organism heals its wounds. That’s the concept behind self-healing asphalt. This innovative technology contains special additives that allow the asphalt to repair its own cracks over time.
This whole service is akin to having a maintenance crew built into the asphalt itself, which can significantly slash maintenance costs and extend the lifespan of paved surfaces.
Eco-Friendly Asphalt Solutions
In the face of pressing environmental concerns and the impact of crude oil, the asphalt industry is stepping up with eco-friendly solutions. Innovations from companies like foamix asphalt incorporate reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) to create low-energy, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly asphalt mixes.
The use of Warm Mix Asphalt (WMA) offers several benefits, including:
- Reduced energy consumption
- Improved working conditions by minimizing exposure to fuel emissions, fumes, and odors
- High-quality, environmentally conscious solutions
These eco-friendly solutions are testament to the industry’s commitment to meeting various project specifications.
Real-World Applications of Asphalt Material

From the roads we drive on to the roofs that shelter us, asphalt’s versatility shines through in its myriad applications. It’s used in:
- Paving roads, both rural and urban, in the United States
- Airport runway construction, thanks to its ability to endure extreme load conditions and temperature variations
- Agricultural settings
- Constructing smooth and durable racetracks
Urban Roadway Projects
Asphalt is the unsung hero of urban infrastructure. In cities, it provides a durable, skid-resistant surface for bus lanes, bike paths, and pedestrian walkways. Whether it’s a bustling city freeway or a quiet suburban lane, asphalt’s role in urban roadway projects is pivotal, ensuring safe and efficient mobility for all.
Waterproofing and Sealing Applications
Asphalt’s water-resistant properties make it an effective sealant for waterproofing projects. It’s insoluble in water and salt and can resist water penetration with minimal absorption, making it ideal for use as a damp-proof course between the foundation and superstructure in building construction.
So, next time you’re sheltering from the rain in a building, remember, it’s likely that asphalt is playing its part in keeping you dry.
Asphalt Maintenance and Lifecycle
Asphalt, like any other material, requires proper maintenance to ensure its longevity. An effective maintenance strategy goes beyond addressing problems as they arise; it includes preventative measures aimed at extending the lifespan of asphalt pavements.
A well-maintained asphalt pavement can serve customers for up to twenty years, making preventative maintenance more cost-effective in the long run compared to corrective or emergency maintenance.
Preventative Maintenance Strategies
Preventative maintenance for asphalt pavements is akin to regular health check-ups. Just as regular check-ups can help detect health issues before they become serious, preventative maintenance strategies, services such as regular sweeping and sealcoating, can help maintain asphalt appearance and longevity.
Addressing larger cracks through filling is also crucial, as neglecting them can lead to significant damage. Such proactive maintenance guarantees the long-term health and longevity of asphalt pavements.
The Benefits of Asphalt Recycling
Asphalt recycling is a win-win situation. It offers both environmental and economic benefits, including reduced waste, conservation of resources, and improved pavement performance. Recycled asphalt pavement (RAP) has been tested for improved stiffness and durability over traditional pavement, leading to less required maintenance and prolonged infrastructure life.
From roads to residential and commercial roofing and landscaping, the benefits of asphalt recycling are being felt across various constructions, enhancing environmental sustainability.
Summary
From its composition to its real-world applications, the journey of asphalt is a testament to human ingenuity. Its unique blend of aggregates, binder, and filler provides a sturdy and durable material for various applications. Innovations like self-healing asphalt and eco-friendly solutions are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, while careful quality control and preventative maintenance strategies ensure its longevity. As we continue to innovate and improve, the future of asphalt looks promising, paving the way for safer, more efficient, and sustainable infrastructures.
Certified MTP has an elite selection of Mix Marshall Design tools and equipment, showcasing industry-leading brands for Marshall Stability Test Systems, Marshall Compactor Test Equipment and Molds, Marshall Water Baths for Asphalt Testing, Asphalt Mix Design Equipment, Asphalt Pavement Testing Equipment, and Sample Ejectors for Asphalt Extrusion.
Frequently Asked Questions
What asphalt is used on roads?
Hot mix asphalt is the most commonly used asphalt on roads and pavements, known for its flexibility and weather-resistant properties.
What is new asphalt made of?
New asphalt is mainly made of bitumen combined with aggregate like sand or gravel.
Is asphalt the same as blacktop?
Yes, blacktop is a type of asphalt, but the difference between the two lies in how they are mixed and prepared, which is determined by their specific usage.
Where is asphalt made from?
Asphalt is made from a semi-solid form of petroleum, which includes a mixture of crushed stone, gravel, sand, and a sticky byproduct called bitumen. The sticky black residue is a leftover from the processing of crude oil.
What are the different types of asphalt mixes?
There are three major types of asphalt mixes used for paving: hot, warm, and cold, each designed to meet specific project needs and performance requirements.
Related Blogs for Asphalt Material:
Top Asphalt Testing Solutions for Pavement Performance
Asphalt Testing Equipment: A Comprehensive Guide
Mastering Marshall Testing: A Guide for Quality Asphalt
Benefits of Asphalt Mixer: Mixing Asphalt for Construction
All You Need to Know About Asphalt Thermometers
Asphalt Testing: Equipment, Solutions, and Engineering
The Importance of Asphalt Density in Pavement Construction
Asphalt Depth Poker – A Comprehensive Guide
Asphalt vs Concrete: A Comparative Study
Ignition Oven: A Guide to NCAT Asphalt Content Furnace Tech
Discover the Best Asphalt Core Drill Bit for Your Project
Benefits of Asphalt Binder: A Comprehensive Guide
Rice Testing: Guide to Asphalt Specific Gravity Testing
The Best Guide to Coring Test for Asphalt & Concrete Cores
Understanding the Marshall Test for Asphalt Mix Design
Understand Viscosity of Asphalt: Dynamic and Kinematic
Essential Asphalt Testing for the Road Surface
Asphalt Testing Equipment: A Comprehensive Guide
Asphalt Rice Testing: Understanding the Equipment and Tests
Understanding the Specific Gravity of Asphalt
Factors That Influence the Quality of Asphalt: 21 Keys
Determining the Specific Gravity of Asphalt with Rice Test
Marshall Test: Comprehensive Guide to Asphalt Testing
Five Asphalt Repair Tips for Surfaces to Save Time and Money
Asphalt Testing: From Materials Testing Experts
Top Choice for Bulk Rubber Hose: Durability And Flexibility
Choosing Asphalt Tester: Guide to Reliable Pavement Tests
Asphalt Thermometers: All You Need to Know
What Is Asphalt Made Of: Guide to Composition and Quality

