Converting from Kelvin to Rankine? Straightforward and quick. This article breaks down the K to Rankine conversion process, along with detailed explanations, calculation tools, and tables to make sure you get accurate results every time. Whether you’re a student, engineer, or enthusiast, learn how the scales compare and put them to practical use.
Key Takeaways
- The K to Rankine conversion calculator is a precise tool that allows for customizable accuracy through adjustable significant figures for converting between the Kelvin and Rankine temperature scales.
- K to Rankine conversion is a straightforward process based on multiplying the temperature in Kelvin by 1.8 and accounting for the distinct zero points of both scales to ensure precision.
- Both Kelvin and Rankine are absolute temperature scales with real-world applications in fields like astronomy and electronics, and accurate conversion between these scales is crucial for scientific accuracy and technical applications.
K to Rankine Conversion Calculator
The K to Rankine conversion calculator offers a simple and accurate method for converting temperatures between these two scales, including the kelvin to rankine conversion. The calculator combines a user-friendly design with customizable accuracy options, allowing for precision tailored to your needs. Additionally, the rankine to kelvin conversion is just as straightforward and precise.
The precision of conversion results depends on the number of significant figures employed. You can adjust the number of significant figures on this calculator to suit your precision needs, guaranteeing highly accurate results.
How to use the K to Rankine calculator
The K to Rankine calculator boasts a simplistic design. Start by entering your temperature in Kelvin in the input field labeled “Kelvin”. Once you’ve entered the temperature, click on the “Convert” button to initiate the convert kelvin process.
The calculator is designed to:
- Round the answer to the correct number of significant figures based on your input’s precision
- Guarantee highly accurate results
- Offer you dependable data for your temperature computations.
Mastering the K to R Formula
The process of converting k to ranking is based on a straightforward formula. To convert from Kelvin to Rankine, simply multiply the temperature in Kelvin by 1.8. This can alternatively be expressed as °R = K * (9/5), which reaffirms the multiply-by-1.8 rule. Additionally, to convert kelvin and rankine to other temperature scales, you can follow similar conversion methods.
It’s important to comprehend that the degrees on the Rankine scale match those on the Fahrenheit scale, unlike the Kelvin scale, which corresponds to Celsius degree sizes. The complete formula for converting Kelvin to Rankine is therefore articulated as Rankine = (Kelvin × 1.8) + 459.67, incorporating the conversion factor and a constant.
Understanding the Conversion Process
The Kelvin and Rankine temperature scales are both absolute scales, meaning they start from absolute zero. However, they differ in their unit sizes and starting points. When converting from Kelvin to the temperature in Rankine, the temperature in Kelvin is first multiplied by 1.8.
The subsequent step in the conversion involves adding 459.67 to the result. This adjustment accommodates the distinct zero points of the Kelvin and Rankine scales, guaranteeing a precise conversion.
Dive into Kelvin Scale
The Kelvin scale, which was proposed in 1848, serves as the base unit for temperature in the International System of Units (SI). It has become the standard for scientific measurements. Its absolute characteristic positions it as an essential tool for achieving precision and consistency in scientific temperature measurements. The scale starts from absolute zero, a fundamental aspect for many scientific fields including physics and engineering.
In 2019, the Kelvin scale was redefined, linking zero points of it to the exact value of the Boltzmann constant. This enhanced the accuracy of temperature measurements across various conditions without reliance on physical artifacts. Today, the Kelvin scale’s use is widespread in engineering and physical sciences, serving as the primary unit of temperature due to its straightforward conversion to other scales.
Absolute Zero and Beyond
At the heart of the Kelvin scale is the concept of absolute zero, also known as the zero point. This is the point where a system has no thermal energy, signifying the complete absence of heat. At a freezing point of absolute zero or 0 Kelvin K (-273.15°C), a system theoretically reaches its lowest energy state, with the volume of gases reducing to zero as per Charles’s law and heat removal becoming infinitely challenging.
Scientific endeavors near absolute zero have revealed unusual properties of matter such as superfluidity and Bose-Einstein condensation, illuminating obscure aspects of the quantum realm. In temperature unit conversions, it’s imperative to recognize that 0 K and 0 °R both represent absolute zero to avoid potential technical mishaps due to misinterpretation.
Unraveling Rankine Scale
The Rankine scale, also known as the rankine temperature scale, was proposed by the Scottish engineer and physicist Macquorn Rankine in 1859. Like the Kelvin scale, it’s an absolute temperature scale, but it uses Fahrenheit increments instead of Celsius. This means that converting Fahrenheit to Rankine is straightforward, as a change of 1°R is equivalent to a change of 1°F.
The Rankine scale is particularly favored in the fields of engineering and thermodynamics, especially in industries in the United States where heat computations are often performed in degrees Fahrenheit. The rankine scale itself is denoted as °R or °Ra, and its use is common among engineers working with systems calibrated in Fahrenheit, who often refer to it as degrees Rankine.
Boiling and Freezing Points in Rankine
Understanding the boiling point and freezing points of water in Rankine is critical for accurate temperature measurements and conversions. Here are the key points to remember:
- The freezing point of water is 491.67 °R on the Rankine scale.
- This value plays an integral role in multiple scientific calculations.
- It can be utilized as a reference when employing the Rankine scale.
Similarly, knowing the boiling point of water in Rankine is important for various scientific and engineering applications. Under standard atmospheric pressure, water boils at 671.64102 °R in the Rankine scale. This boiling point in rankine can be an important reference when carrying out temperature conversions and calculations.
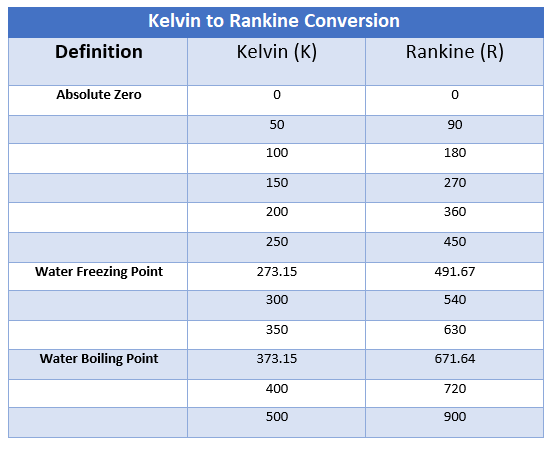
K to Rankine Conversion Table
For those who frequently convert temperatures between Kelvin and Rankine, a conversion table can be a handy tool. From 0 K (which is equivalent to 0 °R) to 1000 K (equivalent to 1800 °R), the table provides quick and easy conversions for various temperature values.
These conversion tables serve as handy quick references and can also validate the accuracy of your manual conversions or computations performed with a conversion calculator. Whether you are an engineer, a student, or a researcher, a Kelvin to Rankine conversion table can greatly facilitate your work.
Practical Applications of K to Rankine Conversion
Understanding how to convert between Kelvin and Rankine is not just an academic exercise. It has real-world implications in various scientific and engineering disciplines. In astronomy, for instance, Kelvin is crucial for classifying stars and gauging their surface temperatures. Therefore, converting Kelvin to Rankine is important for studies involving celestial temperatures, like the Sun’s photosphere with its temperature around 5772 K.
In the field of electronics, Kelvin is often used in engineering, as an indicator of circuit noise, known as noise temperature. Thus, converting temperatures from Kelvin to Rankine is pertinent for maintaining precise noise assessments. Furthermore, the discovery of superconductivity near absolute zero (measured in Kelvin) underscores the importance of Kelvin to Rankine conversion for applications like MRI detectors and particle accelerators.
Troubleshooting Conversion Errors
Although the conversion of temperatures from K to Rankine appears uncomplicated, there are prevalent mistakes that might result in inaccuracies. One such error is confusing the Rankine temperature scale used with the Kelvin scale, which can lead to erroneous results due to incorrect assumptions about the relationship between the two scales. Another common oversight is failing to adjust for the different zero points on the Kelvin and Rankine scales, which is critical to accurate conversions.
To prevent errors from being carried through the calculation, follow these steps:
- Verify that the starting temperature in Kelvin is accurate before applying the conversion formula.
- Label the unit of the result as Rankine (R) after conversion to avoid confusion with other temperature scales.
- Remember that significant figures play a key role in precision, and it’s necessary to understand their rules to ensure accurate rounding.
By following these steps, you can ensure accurate temperature conversions.
Utilize reliable resources such as conversion calculators, conversion tables, or specialized apps to avert conversion errors and prevent common blunders.
Summary
Navigating the Kelvin and Rankine temperature scales and their conversions doesn’t have to be a daunting task. With a solid understanding of the scales, knowledge of the conversion formula, and the right tools at your disposal, you can effortlessly convert temperatures from K to Rankine. Whether you’re an engineer, a scientist, a student, or simply a curious mind, mastering these scales will undoubtedly enhance your understanding of the fascinating world of temperature.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the formula of Kelvin to Rankine?
To convert Kelvin to Rankine, you can use the formula R = K × 9/5.
How do you convert R to K?
To convert a temperature from Rankine to Kelvin, you can use the formula: T(K) = T(°R) * (5/9).
What is the formula for degree to Rankine?
To convert degrees Celsius to degrees Rankine, use the formula: (°C x 9/5) + 491.67. For instance, if the temperature is 25 degrees Celsius, the calculation would be (25 x 9/5) + 491.67 = 536.67 Rankine.
What is the difference between Kelvin and Rankin?
The difference between Kelvin and Rankin is that while both have their zero set to absolute zero, Kelvin uses the same degree size as Celsius, while Rankine uses the same degree size as Fahrenheit. This means that a change of 1 degree in Rankine is the same as a change of one degrees celsius or 1 degree in Fahrenheit, while in Kelvin it’s a change of 1 degree in Celsius.
What is absolute zero on the Kelvin scale?
Absolute zero on the Kelvin scale is 0 K, which is equivalent to -273.15°C. At this point, a system theoretically has no thermal energy.
Related Blogs for K to Rankine:
Thermometers with Mercury: Everything You Need to Know
Precision ASTM Thermometers: Certification and Specification
How to Convert 65 Degrees C to F>
Role of Thermometers in Concrete Curing
How to Convert 70 Deg F to C Easily
How to Convert 158 Fahrenheit to Celsius (158 F to C)
Lab Grade Thermometer for Concrete Testing
Certified Thermometers for Material Testing
Comprehensive List of Biology Laboratory Equipment in 2023
Thermometers Calibrated: Calibrate for Accurate Readings
Convert 900 Degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius (900 F to C)
Master C to F Formula: How to Convert Celsius to Fahrenheit
Digital Humidity and Temperature Meter: Discover the Best
7 Fahrenheit to Celsius: Quick Temperature Conversion Guide
75 Fahrenheit to Celsius Converter: Easy Conversion Method
Easy Guide: Convert 69 Fahrenheit to Celsius Effortlessly
67 F to C: Accurate Fahrenheit to Celsius Conversion Guide
Convert 99.4 F to C: Fahrenheit to Celsius Conversion
Easy K to F Conversion: Your Guide to Kelvin to Fahrenheit
Quick 35 f to c Conversion: Convert Fahrenheit to Celsius
Easy 0 F to C Conversion: Turn Fahrenheit into Celsius Fast
60 Degrees C to F: Quick Conversion Guide
32 Celsius to Fahrenheit: Easy Temperature Conversion Guide
How to Convert 79 Degrees F to C Easily [Conversion Solved]
Temperature Conversions Table: Fahrenheit to Celsius
Celsius to Kelvin: Guide to Accurate Temperature Conversion
Quick and Easy Celsius Calculator for Temperature Conversion
Fahrenheit to Rankine Formula: Steps for Temp Conversion
Easy Guide: Convert 69 Fahrenheit to Celsius Effortlessly
Best Thermometer for Humidity: Guide to Accurate Readings
Humidity Testing: Product Reliability and Performance
Calculate Heat Index: Understanding the Feel of Temperature
Best Thermometer for Humidity: Guide to Accurate Readings
Degrees in Radians: A Guide for Converting Angles
Conversiones de Temperatura: Convierte Celsius y Fahrenheit