The world of primary crushing might seem complex, but jaw crushers have proven their worth as a reliable choice in reducing the size of large rocks and ores. With a variety of various crusher types available, each with its own unique features and advantages, it’s essential to understand the differences and make an informed decision when selecting the right crusher for the job. So, let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of crushers.
Key Takeaways
- Crushers are a type of primary crusher used in various industries, consisting of fixed and moving jaws, a crushing chamber, an eccentric shaft, a toggle plate and pitman.
- Factors to consider when selecting a jaw crusher include material properties, feed size and output requirements, and maintenance & operating costs. As well as comparison with other primary crushers.
- Optimizing performance requires proper feeding techniques, regular maintenance & timely replacement of worn parts.
Understanding Crushers
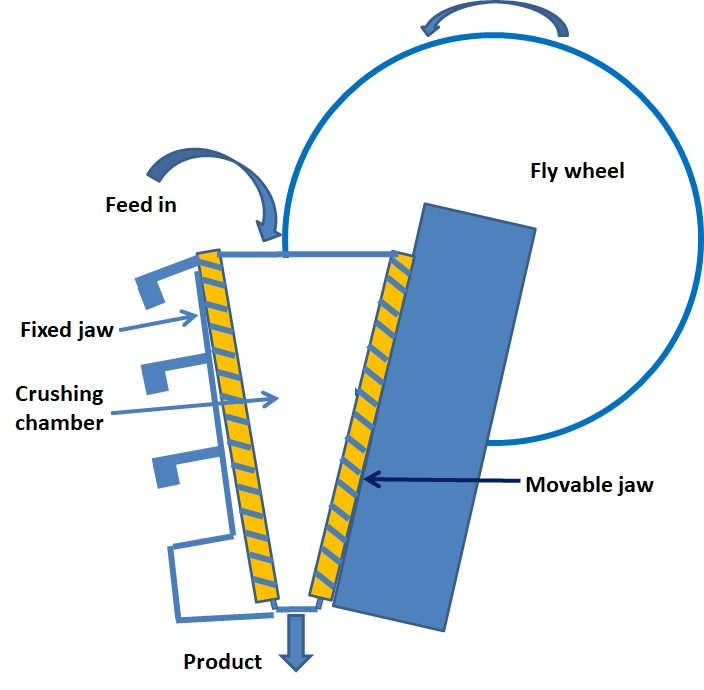
Crushers have been a staple in the mining, construction, and recycling industries for decades. These powerful machines consist of a fixed jaw and a moving jaw, which form the crushing machine chamber. The crushing process involves compressive force, as the moving jaw reciprocates to crush the material against the fixed jaw.
But how do jaw crushers differ from other primary crushers like gyratory crushers and impact crushers? And what are the different types of crushers available? We’ll uncover the answers to these questions.
Components
A crusher is made up of several key components. At its core, the jaw crusher consists of:
- Fixed jaw
- Moving jaw
- Crushing chamber
- Eccentric shaft
The fixed jaw and moving jaw create the crushing chamber where the material is reduced in size. The moving jaw is attached to an eccentric shaft, which causes it to move back and forth against the fixed jaw.
The toggle plate connects the moving jaw to the pitman, the part responsible for the reciprocating motion. As the material is crushed, it moves down the crushing chamber and is discharged once it reaches the appropriate size.
These components work together in harmony to provide a dependable and efficient crushing process.
How Crushers Work
Crushers employ compressive force to break down materials by passing the feed between two solid surfaces. The crushing chamber is formed by the v-shaped area between the two jaws, where the material is subjected to crushing. As the moving jaw applies pressure, the material is broken down and forced through the narrowing space between the jaws, eventually exiting the chamber at the desired output size.
The majority of the crushing action takes place in the bottom third of the chamber, where the material is subjected to the highest compressive forces. The usual crushing ratio of a jaw crusher is between 6:1 and 8:1, resulting in a consistent and efficient reduction in size. The gap between sized material and the jaws at the discharge outlet determines the material output size, which can be adjusted either hydraulically or manually by adding and removing shims. This process is essential for secondary crushing.
Types of Crushers
There are three primary types of crushers available, each offering unique features and advantages: single toggle crushers, double toggle crushers, and overhead eccentric crushers. These three crushers feature and can be used for both primary and secondary crushing applications, making them a versatile choice for various industries.
We’ll examine each type along with their unique advantages.
Single Toggle
Single toggle crushers are characterized by a single moving jaw hinged at the top, allowing for a high reduction ratio and a large feed size capacity. These crushers are commonly used in mining, quarrying, and recycling industries for primary crushing. Renowned for their high efficiency, low maintenance requirements, and long service life, single-toggle jaw crushers are simple to operate and require minimal instruction.
However, they may necessitate more frequent maintenance and may not be suitable for certain applications due to their limited size and capacity.
Double Toggle Crushers
Double toggle crushers, on the other hand, feature two toggle mechanisms to move the blake-type jaw crusher back and forth, resulting in a more uniform crushing action. As opposed to single-toggle crushers, double-toggle jaw crushers possess two shafts and two toggle plates, providing a higher throughput capacity.
They are utilized in various industries, including:
- mining
- construction
- demolition
- quarrying
Double toggle crushers, such as the double toggle crusher, are suitable for processing larger volumes of material and producing a more consistent product with minimal fines.
Overhead Eccentric Crushers
Overhead eccentric jaw crushers have an eccentric shaft located above the crushing chamber, allowing for increased durability and performance. This design permits horizontal shaft of the swing jaw to move at a higher speed and with more force, resulting in a crushing action that is both aggressive and efficient.
Although overhead eccentric crushers require more maintenance and upkeep than other types of jaw crushers, their enhanced performance and durability make them an attractive option for various applications.
Primary Crushing Applications
Crushers are commonly used as primary and secondary crushers in various industries and applications, including mining, construction and demolition, and quarrying. Their versatility and adaptability to different materials make them a popular choice for the primary crushing stage, ensuring that the material is reduced to the appropriate size for further processing.
Let’s explore some of the most common primary crushing applications where jaw crushers excel.
Mining Industry
In the mining industry, crushers are used for the primary crushing of various ores and minerals, such as gold, copper, and iron. The high efficiency, dependability, and resilience of crushers make them a popular choice for mining operations, as they can handle large quantities of material and are well-suited for hard, abrasive materials.
Choosing a crusher for mining applications calls for a careful evaluation of factors like material properties, feed size, output requirements, and upkeep costs.
Construction and Demolition
Crushers play a crucial role in the construction and demolition industries, where they are used for the primary crushing of concrete and other materials. Their high efficiency, reliability, and durability make them an ideal choice for breaking down large chunks of material on construction and demolition sites.
For construction and demolition applications, consider factors like material properties, feed size, output requirements, and upkeep costs when choosing a jaw crusher.
Quarrying
In the quarrying industry, crushers are used for the primary crushing of rocks and aggregates, such as limestone, granite, and basalt. These powerful machines can handle a variety of materials, making them an ideal choice for processing large volumes of material in rock quarries, sand and gravel operations, and mining sites.
Choosing a crusher for quarrying applications requires considering factors like material properties, feed size, output requirements, and maintenance costs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Crusher
When selecting a crusher for your specific application, several factors should be taken into account, including:
- The size of the feed material
- The material type and hardness
- The desired output size
- The capacity
- The cost
Choosing a crusher demands careful consideration. It must:
- Handle the material size and type
- Achieve the desired output size
- Meet production requirements
- Maintain manageable upkeep and operating costs.
We’ll further examine these factors and their influence on jaw crusher selection.
Material Properties
The material properties of the material being crushed play a vital role in determining the most suitable jaw crusher for the job. Different materials have distinct properties, and the type of crusher that is most suitable for a given crushed material will depend on its properties. Some factors to consider include:
- Hardness
- Abrasiveness
- Toughness
- Size and shape
- Moisture content
All of these factors play a role in determining which crusher is best suited for the task at hand.
Understanding these material properties can guide you in making an informed decision when selecting a jaw crusher.
Feed Size and Output Requirements
Feed size and desired output size can also impact your choice of crusher. It’s generally recommended to select a crusher with a feed size that is smaller than 80% of the feed opening.
Different crushers have varying capacities and can produce different output sizes, so it’s important to select a jaw crusher that can meet your specific output requirements. Keeping these factors in mind can help you choose the right jaw crusher for your application.
Maintenance and Operating Costs
Lastly, the upkeep and operating costs associated with your crusher are important considerations. This includes:
- Running costs
- Fuel and transport costs
- Wear parts costs
- Energy consumption
Selecting a crusher that is easy to maintain, has a long service life, and is energy-efficient can result in cost savings over time. By taking these factors into account, you can ensure that your crusher not only meets your needs but also remains cost-effective and efficient throughout its lifespan.
Jaw Crusher vs. Other Primary Crushers
Now that we’ve covered the basics of crushers, it’s time to compare them with other primary crushers, such as roll crushers, gyratory crushers and impact crushers. Each type of primary crusher has its own unique set of advantages and disadvantages, which can impact their suitability for specific applications.
We’ll examine how jaw crushers compare to their counterparts.
Jaw Crusher vs. Gyratory Crusher
When comparing jaw crushers and gyratory crushers, it’s important to consider their differences in terms of size reduction, capacity, and material handling.
Here are some key differences:
- Jaw crushers are typically smaller and lighter, making them easier to transport and install, with a lower operating cost.
- Gyratory crushers are larger and heavier, requiring more space and a higher initial investment.
- Jaw crushers have a limited crushing range and are not suitable for large-scale production.
- Gyratory crushers have a larger crushing range and are better suited for high-capacity operations.
Gyratory crushers, on the other hand, are larger and more efficient, capable of handling large quantities of material and producing a more consistent product with minimal fines. However, they come with a higher price tag and require more maintenance.
Another key difference between jaw crushers and gyratory crushers is the size and shape of the crushing chamber. A jaw crusher has a rectangular or square-shaped opening at the top, while a gyratory crusher has a conical-shaped opening. Furthermore, the jaw crusher has a fixed jaw and a moving jaw, whereas the gyratory crusher has a fixed central cone and a rotating mantle.
Consider design variations’ impact on crusher suitability for specific applications. Essential to match crusher type with project requirements.
Jaw Crusher vs. Impact Crusher
Comparing crushers and impact crushers, their differences lie in the reduction ratios, material suitability, and product shape. Jaw crushers typically have a reduction ratio of 6:1 to 8:1, making them ideal for harder materials like granite and limestone.
In the world of crushing equipment, there are various types of crushers available, such as jaw crushers, impact crushers, and cone crushers. Each type fulfills a specific purpose, depending on the material it crushes. Jaw crushers produce a more cuboidal product, while impact crushers yield a flakier or elongated product. Conversely, cone crushers handle harder materials and provide a higher reduction ratio, suiting applications like asphalt and concrete.
Depending on the desired output size and crush material properties, one type of crusher may be more suitable for your application than the other.
Tips for Optimizing Performance
For optimal efficiency and performance from your crusher, adherence to a few simple guidelines and best practices is key. These include using proper feeding techniques, performing regular maintenance, and timely replacement of worn parts.
We’ll discuss these tips in greater detail to maximize your crusher’s potential.
Proper Feeding Techniques
Ensuring proper feeding techniques is crucial for the optimal performance and longevity of your crusher. This means evenly distributing the material and gradually feeding it into the crusher to prevent overloading or bridging.
Inspecting the material for any large pieces that could damage the crusher is also important. By adhering to these proper feeding techniques, you can prevent damage to your jaw crusher and ensure that it operates efficiently.
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for the longevity and optimal performance of your crusher. This includes inspecting the crusher for wear, lubricating the moving parts, and verifying the tension of the toggle plate.
Additionally, it’s important to check the alignment of the crusher and adjust it if necessary to ensure smooth operation. By performing regular maintenance, you can extend the life of your crusher and maintain its efficiency.
Wear Parts Replacement
Timely replacement of worn parts is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and performance of your crusher. This includes jaw plates, liners, and toggle plates, which can wear down over time and impact the crusher’s performance.
Regularly inspecting the condition of these parts and replacing them when necessary can help extend the life of your jaw crusher and ensure optimal performance.
Summary
In conclusion, crushers are versatile and efficient machines that play a crucial role in various industries and applications, from mining to quarrying, construction, and demolition. Understanding the different types of jaw crushers, their unique features, and how they work can help you make an informed decision when selecting the right crusher for your specific application. Considering material properties, feed size, output needs, and maintenance costs ensures cost-effective, efficient jaw crusher operation over time. This comprehensive approach guarantees meeting needs while optimizing performance. Keep these insights in mind, and your crusher will continue to serve you well for years to come.
Certified MTP has an elite selection of lab solutions, showcasing industry-leading brands including Flasks, Beakers, Pipettes, & Graduated Cylinders, Benchtop & Economy Laboratory Mills, Jar Mills, pulverizers and lab crushers, and the popular mini jaw crusher.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a crusher used for?
Crushers serve various industries like construction, recycling, mining, and quarrying, handling large feed sizes and enduring abrasive wear. Their versatility makes them indispensable in multiple applications.
What is the difference between a jaw and a cone crusher?
Crushers primarily crush materials of varying hardness like pebbles, granite, limestone, and barite. Cone crushers then process materials with higher hardness such as granite, river pebble, and basalt for secondary and tertiary crushing. These two types of crushers differ in terms of their processing capacity, production capacity, and final product quality.
What is the output of a crusher?
The output of a crusher is typically a uniform, cubical-shaped material with a size range of 10-350mm, while a cone crusher produces a material with a size range of 5-50mm.
What is crushing?
Jaw crushing is a technique where the reciprocating motion of a movable jaw crushes and compresses rocks or ore between itself and a fixed jaw.
What does a crusher look like?
A crusher consists of two metal plates that come together to form a V-shaped jaw, with adjustable jaws that range from one inch to five inches.
Related Blogs for Jaw Crusher:
Chemistry Glassware Names: A Comprehensive Guide
Suction Filtration: The Basics of Vacuum Filtration
All About Volumetric Flask: Uses, Function & Overview
Aspirator Flask: Benefits of Borosilicate Glass Filter Flask
Understanding Air Condenser Chemistry in 2023
What is a Graduated Cylinder Used For?
Most Accurate Glassware for Measuring Volume
Comprehensive List of Biology Laboratory Equipment in 2023
Everything You Need to Know About Beakers in Chemistry
Portable Rock Crushers for On-Site Crushing
Small Jaw Crusher: Get the Most
Small Jaw Crushers for Sale: Portable Crushing Machines
Crusher Rock: Exploring the Different Types of Rock Crushers
Grinding Coal Crushers with Charcoal Powder Grinder Machines
Get the Best Jaw Crusher for Your Needs
Soil Pulverizer: Unlock the Benefits