When precision counts, mastering serological pipetting is non-negotiable. This comprehensive guide offers a deep dive into serological pipetting techniques, maintenance, and troubleshooting—tools you need to ensure accurate and reproducible results in your lab work.
Key Takeaways
- Serological pipetting is an essential tool in laboratories for measuring, transferring, and dispensing fluids with high accuracy and come in various types, including glass and plastic, to suit different applications and handling requirements.
- To achieve accurate and precise measurements with serological pipetting, proper usage techniques—such as alignment of the meniscus, temperature equilibration, and regular calibration—are critical, along with using appropriate accessories like bulbs and pumps.
- Maintaining sterility and preventing contamination is imperative when working with serological pipetting; this includes using sterilized tips, following strict cleaning protocols, and selecting the correct pipette type for the desired level of accuracy and application needs.
Understanding Serological Pipetting
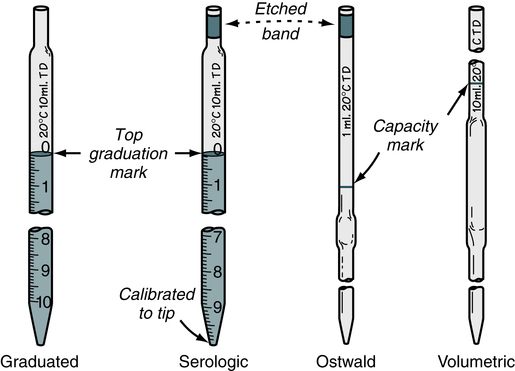
Laboratories use specialized tools called serological pipettes for accurate fluid dispensation. These instruments, usually made of glass pipettes or plastic, come pre-sterilized and feature gradations for measuring aspirated or dispensed volumes.
The main functions of serological pipettes include:
- Transferring liquids
- Mixing solutions
- Layering chemicals of varying densities
- Maintaining sterility
These versatile tools lend themselves to various applications in the laboratory, making them indispensable in a broad range of experimental settings, including the handling of chemical solutions.
Types of Serological Pipettes
Serological pipettes come in different forms, each designed to cater to specific needs. Glass serological pipettes, for instance, are reusable and can be sterilized by autoclaving, making them ideal for applications where sterilization is critical. On the other hand, disposable plastic serological pipettes are preferred for their convenience and safety, reducing the need for cleaning and sterilization.
Certain designs have been developed to handle specific tasks. Here are some examples:
- Open-end pipettes: designed for high viscosity liquids like oils or cosmetics
- Bacteriological pipettes: adhere to specific public health standards, making them ideal for examining dairy products
- Serological pipettes: the choice of type is influenced by the nature of the liquid being handled and the specific requirements of the experiment.
Proper Use of Serological Pipettes
Using a serological pipette effectively requires more than just knowledge of its function; it demands mastery of technique and continuous learning. Selecting a pipette with an ergonomic design is essential for manual protocols to reduce fatigue and minimize errors during repetitive pipetting procedures.
Skill improvement and continuous learning are recommended to enhance pipetting proficiency. This ensures that laboratory results rely on accurate and precise measurements, making it crucial to understand the correct usage of pipettes and continuously refine these skills.
Serological Pipette Accessories: Bulbs and Pumps
Just as important as the pipette itself are the accessories that come with it. Accessories such as bulbs and pumps play a crucial role in the efficient and effective use of serological pipettes. Pipette bulbs, for instance, are used with glass serological and pipettes can be used for transferring non-specific liquid volumes.
On the other hand, pipette dispensers, particularly the pipet-aid, are commonly used for serological pipettes. They have aspirating and dispensing triggers with speed control settings, while fit motorized pipettes offer improved ergonomics, reduced pipetting time, and increased productivity. These accessories, including the pipette pump, when used properly, can significantly enhance precision in fluid transfer, making them indispensable tools in the laboratory.
Accuracy and Precision in Serological Pipetting
Accuracy and precision are the cornerstone of any scientific experiment. Factors such as liquid density, temperature, and environmental conditions affect serological pipetting accuracy. Serological pipettes must deliver liquids with an accuracy of +/- 2% and undergo calibration at 20 degrees Celsius, representing the temperature for measuring accurate milliliter volumes.
Regular calibration is essential for serological pipettes, which should be conducted annually or whenever calibration drift is suspected to ensure precision in measurements. Moreover, thermal transfer from hands to pipette can compromise accuracy; hence, equilibrating temperatures between all pipetting components is important to maintain accurate results.
For accurate pipetting, one must use the correct technique, including pre-wetting the tip, holding the pipette vertically, and ensuring the last drop is blown out, following the manufacturer’s directions for maintenance. Maintaining the accuracy and precision of serological pipettes requires regular performance checks and adherence to calibration procedures to reduce the risk of errors and contamination.
Reading Volumes and Measurements with Serological Pipettes
Accurate measurement is paramount in laboratory work, especially when dealing with milliliter volumes. When using a serological pipette, follow these steps to ensure precision:
- Align the bottom of the concave liquid surface, or meniscus, with the desired graduation mark.
- To measure a specific volume, draw the liquid slightly above the target graduation.
- Gently lower the liquid to align the meniscus with the line.
- View the meniscus at eye level to ensure precision.
By following these steps and transferring accurate milliliter volumes, you can ensure accurate measurements in your laboratory work.
During liquid aspiration, follow these steps to ensure accurate measurements:
- Immerse the pipette tip only slightly, about 2-3mm, to avoid drawing up air or creating bubbles.
- Hold the pipette vertically to draw the liquid evenly.
- Prevent liquid from adhering to the outside of the pipette by not submerging the tip too deeply during aspiration.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure precise and reliable liquid aspiration.
Clean the outer surface of the pipette tip with a non-fibrous tissue before adjusting to the meniscus as a regular practice to improve volume accuracy.
Fluid Dispensation and Aspiration Techniques
Dispensing and aspirating fluids accurately, especially when transferring milliliter volumes, is an art that requires mastery of specific techniques. When dispensing fluids, gently touch off the pipette tip to the side of the receiving vessel and avoid splashing by controlling the release of the push-button. For precise aspiration, pre-wet the pipette tip, submerge it no more than 1-2mm into the liquid, and maintain a consistent speed for error-free liquid uptake.
Preventing air bubbles and aerosol formation is key to accurate pipetting and avoiding fluid contamination when mixing chemical solutions. This can be achieved by pre-wetting the tip, releasing air pressure from the plunger slowly, and ensuring consistent pressure when attaching the tip.
Accuracy and precision are further improved when blowing out the complete liquid, ensuring that the tip is properly conditioned, the plunger’s pressure is controlled, and a fiber filter plug is used.
Maintaining Sterility and Reducing Contamination
Sterility and contamination prevention are crucial aspects of laboratory work. When using serological pipettes, it’s important to:
- Prevent contamination by ensuring a tight seal with nearly all pipette controllers
- Change pipette tips after each sample
- Utilize tips with the appropriate purity class and sterilization
Sterility can be maintained through the following methods:
- Thorough hand washing before and during laboratory procedures, using antiseptic soap
- Applying proper sterilization methods like autoclaving and the use of appropriate disinfectants
- Establishing and maintaining a sterile field using a Bunsen burner flame to minimize microorganism influx
- Disinfecting work surfaces
- Proper storage and disposal of materials
The use of high-quality, pre-sterilized pipettes and tips can further minimize contamination.
Choosing the Right Serological Pipette for Your Needs
Choosing the right serological pipette is an important decision that can greatly affect the accuracy of your measurements. The volume range is a critical factor when choosing a serological pipette; ensure the pipette volume is aligned with the application’s required volume.
Using the smallest possible pipette for the job helps in reducing errors and improving accuracy. Serological pipettes come in TC and TD types, affecting the method by which the specified volume is delivered. For accurate and precise liquid transfer, choose serological pipettes that offer the desired level of accuracy, with some offering 1-2% accuracy.
Serological Pipettes vs. Other Pipettes: A Comparison
Serological pipettes, while versatile, are not the only type of pipette used in laboratories. For instance, micropipettes use disposable tips and work on the principle of air displacement, making them suitable for handling smaller volumes than serological pipettes.
Fixed volume pipettes, on the other hand, are chosen for consistent volume delivery needed in clinical diagnostics and quality control, while serological pipettes allow variable volume transfer which is advantageous in a broader range of experiments. It’s important to understand the differences in order to choose the most appropriate pipette for your specific needs.
Troubleshooting Common Serological Pipetting Issues
Like any tool, serological pipettes can present challenges and issues that require troubleshooting. Leakage during pipetting can occur due to damaged or worn-out parts, incorrect tip fitting, air bubbles, or improper technique. These issues can be mitigated by inspecting and replacing faulty parts, securing tips properly, and employing consistent pipetting speed and angle.
To deliver the entire contents from a serological pipette, follow these steps:
- Perform a ‘blow-out’ by giving a firm puff of air from the pipette aid to ensure no liquid retention.
- When facing pipetting issues, promptly identify the problem.
- Check for visible defects in the pipette.
- Adjust calibration and settings as needed.
Maintaining crucial records of troubleshooting steps and outcomes is imperative, promptly reporting any unresolved issues to a supervisor or the manufacturer to uphold pipette functionality and ensure quality lab results.
Summary
Serological pipettes are an integral part of laboratory work, with their precision and accuracy playing a pivotal role in the quality of results. Understanding their function, proper use, and the techniques for fluid dispensation and aspiration are key to mastering their use. Regular calibration, maintaining sterility, and reducing contamination are also crucial. Knowledge of different types of pipettes and the ability to troubleshoot common issues can enhance your laboratory skills. The journey to mastery may be complex, but with the right knowledge and skills, it is certainly achievable.
Certified MTP has an elite selection of lab solutions, showcasing industry-leading brands including Flasks, Beakers, Pipettes, & Graduated Cylinders, Filter Funnels, Erlenmeyer Flasks, Measuring Pipettes, Mohr Pipettes, Stainless Steel Beakers, Glass Graduated Cylinders, and Plastic Graduated Cylinders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between serological and volumetric pipettes?
The main difference between serological pipets and volumetric pipettes is that volumetric pipettes are calibrated to deliver a specific volume of a solution through free drainage, whereas serological pipettes are typically calibrated all the way to the tip, and the final drop of the solution has to be blown out.
Why is the serological pipette more accurate?
The serological pipette is more accurate because it is optically optimized with clear ascending and descending graduations, making it easier to read measurements in various activities such as aliquoting. This allows for increased accuracy in dispensing consistent volumes into multiple tubes.
What is the point to point use of a serological pipette?
Serological pipettes are used for mixing chemical solutions, mixing cell suspension, transferring liquids, and accurate measurements of liquid. They are versatile tools in the laboratory.
How do you handle a serological pipette?
Handle a serological pipette by first checking the liquid column for its quality, then drawing the solution, adjusting the liquid level, and releasing the solution. Additionally, gently squeeze the exhaust valve until the bottom of the meniscus touches the desired graduated line, and move the sample to the target container.
What are the main functions of serological pipettes?
Serological pipetting is used for transferring liquids, mixing solutions, layering chemicals of varying densities, and maintaining sterility. These functions make them essential in various laboratory settings.
Related Blogs for Serological Pipetting:
Comprehensive List of Biology Laboratory Equipment in 2023
Chemistry Glassware Names: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Air Condenser Chemistry in 2023
Suction Filtration: The Basics of Vacuum Filtration
What is a Graduated Cylinder Used For?
Most Accurate Glassware for Measuring Volume
All About Volumetric Flask: Uses, Function & Overview
Aspirator Flask: Benefits of Borosilicate Glass Filter Flask
Everything You Need to Know About Beakers in Chemistry
Pipette or Measuring Cylinder: Tools for Liquid Measurements
Measuring the Volume of Liquid: Tips, Tools, and Techniques
Understanding What Are Pipette Tips Used For
Top-Quality Chemical Glassware for Precision Lab Work
Guide to Pipettes: Functions, Types, and Usage Tips
How Many Ounces in a Gallon [Conversion Solved]
Convert Inches Cubed to Feet Cubed [Easily Solved]
Calculate the Wt of Water per Cubic Foot: Quick Guide
Convert Cu Ft of Water to Gallons [Effortless Guide]
Advantages of Mohr Pipette: Precision Measuring Simplified
Best Graduated Cylinder for Accurate Measurements
How Erlenmeyer Flask is Used for Laboratory Applications
Exploring Precision of 100 ml Graduated Cylinder
25ml Graduated Cylinder Choices: Measuring Simplified
Master How to Use Micropipette: Guide for Lab Measurements
Best Volumetric Pipette Bulb: Master Precise Liquid Handling
Price of Micropipette: Cost Guide for Lab Essentials
Mastering Micropipetting: Techniques for Lab Work
How to Read Micropipette Volumes Accurately
Pipette Tip Selection Guide for Precise Lab Measurements
What Are Pipettes: Tools for Precision Liquid Handling
Mohr Pipette Use in the Lab: Accurate Liquid Measuring
Best Pipette Website for Lab Needs – Quality & Precision
Measuring Volume Tools: Guide to Accurate Liquid Measurement
Graduated Cylinder Sig Figs: Precision in Liquid Measurement
Choosing the Best Transfer Pipets for Your Lab Needs
Pipette vs Pipet: Uncovering Differences for Lab Accuracy
Pipetted: Master the Art of Precise Liquid Handling
Flawless Pipetting: Mastering Strategies for Precision
Graduated Pipette Use: Tips for Accurate Lab Measurements
Top Quality Pasteur Pipettes for Precision Liquid Handling
Best Serology Pipette: Guide to Precision Liquid Handling
Top Quality Large Glass Funnel for Efficient Laboratory Use
Best Fritted Buchner Funnel for Laboratory Filtration
Best Filter Funnel Selection for Efficient Liquid Filtration
Scientific Glass Pieces: Bong and Rigs for Connoisseurs
Exploring Type of Beaker: Guide to Laboratory Glassware
Beaker with Measurements for Accurate Liquid Handling